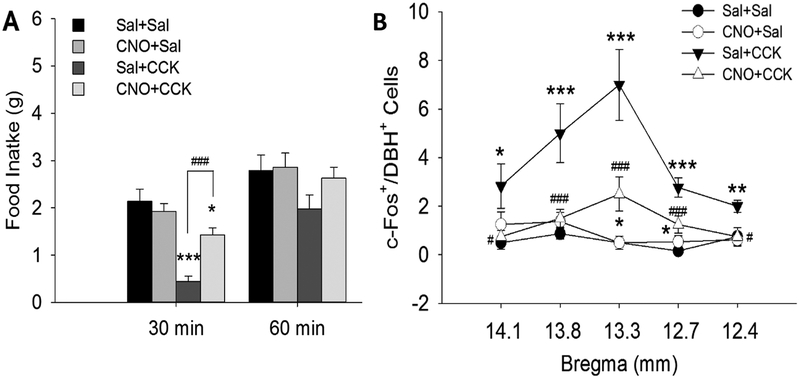
Fig. 11.
Effects of CCK and the DREADD agonist, clozapine- N-oxide (CNO), on food intake and c-Fos expression in NE neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract after A1/C1 transfection with AAV2DIO-hMD3. Rats were food deprived overnight (18 hrs) and then treated with the following drug combinations: Sal+Sal, CNO+Sal, Sal+CCK, CNO+CCK. A, Food intake was suppressed during the 30 min post-injection period in Sal+CCK injected rats, compared to Sal+Sal, but was not suppressed after CCK+CNO injections. B, Cell counts of double stained (c-Fos/DBH) cells are shown at five rostrocaudal levels of the NTS (~14.1, 13.8, 13.3, 12.9 and 12.5 mm caudal to bregma), indicated on X axis. c-Fos in NTS CA neurons was increased 90 min after CCK in Sal+CCK treated rats, but not after CNO+CCK treatment. Data shown are mean ± SEM from 3 – 4 rats/treatment. n = 6 – 8 sections/group/subregion (n = 9 – 12 sections for NTS at bregma −12.9 mm). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. Sal+Sal; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, CNO+CCK vs. Sal+CCK. (by post hoc Student-Newman-Keuls test after two-way ANOVA). Data indicate that both CCK’s satiety effects and its activation of A2 CA neurons is suppressed by CNO activation of A1/C1 CA neurons, even in the absence of glucoprivation. Li, A. J., Wang, Q., & Ritter, S. (2018a). Activation of catecholamine neurons in the ventral medulla reduces CCK-induced hypophagia and c-Fos activation in dorsal medullary catecholamine neurons. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00107.2018