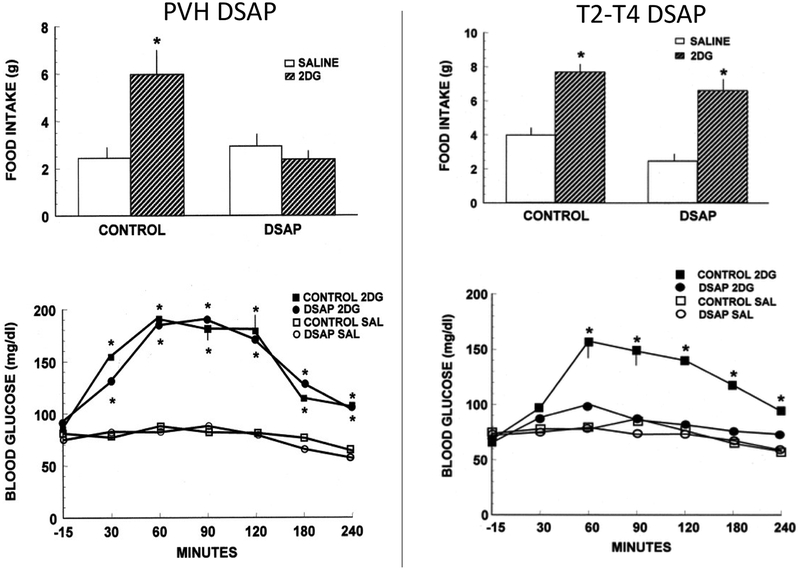
Figure 3.
Intake of pelleted rat chow (top panels) in 4-hour tests after subcutaneous administration of 2DG (200 mg/kg) or saline in rats injected previously into the PVH or spinal level T2-T4 with DSAP or control solution. 2DG or saline injections were given immediately before presentation of food. Means and standard errors are shown. PVH DSAP, but not spinal DSAP injections abolished 2DG-induced feeding. Bottom panels show blood glucose concentrations after subcutaneous administration of 2DG (200 mg/kg) or saline in the same rats as above. 2DG or saline injections were given 15 minutes after the first blood sample was drawn. The hyperglycemic response was tested in the absence of food. Means and standard errors ≥ 10 mg/dl are shown. PVH DSAP did not alter 2DG-induced hyperglycemia. Spinal cord DSAP abolished 2DG-induced hyperglycemia. *, P < 0.001 compared with saline baseline in the same group. (Ritter, S., Bugarith, K., & Dinh, T. T. (2001). Immunotoxic destruction of distinct catecholamine subgroups produces selective impairment of glucoregulatory responses and neuronal activation. J Comp Neurol, 432(2), 197–216.)