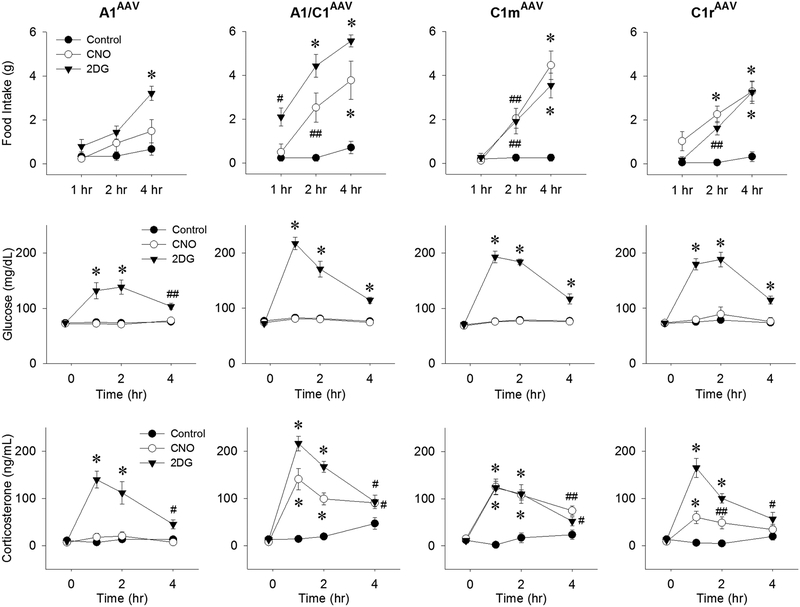
Figure 6.
Responses of male Th-Cre+ transgenic rats to activation of CA neurons at different rostrocaudal levels of the VLM to systemic injection of the glucoprivic agent 2DG or the DREADD receptor agonist clozapine-N-oxide (CNO). Rats were transfected bilaterally by injection of AAV-hM3D into A1, A1/C1, C1m, or C1r. Responses were measured approximately 5 weeks after transfection during the 4-hour period following injection of control (0.9% saline intraperitoneally), CNO (1 mg/kg intraperitoneally), or 2DG (250 mg/kg subcutaneously). Food intake, blood glucose, and plasma CORT levels are shown in the upper, middle and lower panels, respectively. Food intake and CORT levels were increased maximally by CNO in rats transfected at specific VLM sites, but glucose was not altered in rats transfected at any single site. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; *P < 0.001 vs saline control at the same time points by post hoc Student-Newman-Keuls test after two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (six to eight rats for each treatment). Li, A. J., Wang, Q., & Ritter, S. (2018). Selective Pharmacogenetic Activation of Catecholamine Subgroups in the Ventrolateral Medulla Elicits Key Glucoregulatory Responses. Endocrinology, 159(1), 341–355. doi:10.1210/en.2017-00630