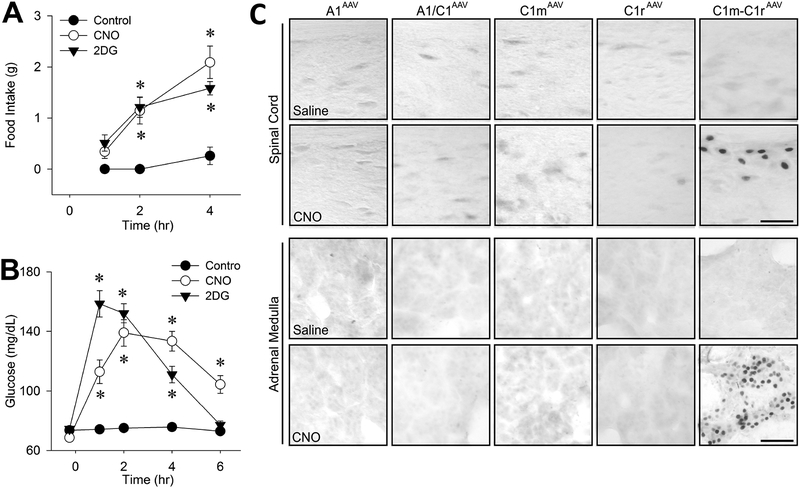
Figure 7.
Food intake (A), blood glucose responses (B) and c-Fos expression in spinal cord and adrenal medulla (C) in female Th-Cre+ rats transfected unilaterally with AAV-hM3D into both C1m and C1r (C1m+C1rAAV-hM3D). In C, VLM injection sites are shown for each column. Tests were conducted approximately 5–9 weeks after transfection. Feeding and glucose responses were measured following administration of control (intraperitoneal saline), CNO (1 mg/kg intraperitoneally) or 2DG (250 mg/kg subcutaneously), using 6–8 rats per treatment. *P < 0.001 vs saline control at the same time point by (post hoc Student-Newman-Keuls test after two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance. cFos in the intermediolateral thoracic spinal cord at T6 and in adrenal medulla were evaluated 2 hrs after intraperitoneal saline or CNO (1 mg/kg intraperitoneally). Li, A. J., Wang, Q., & Ritter, S. (2018). Selective Pharmacogenetic Activation of Catecholamine Subgroups in the Ventrolateral Medulla Elicits Key Glucoregulatory Responses. Endocrinology, 159(1), 341–355. doi:10.1210/en.2017-00630