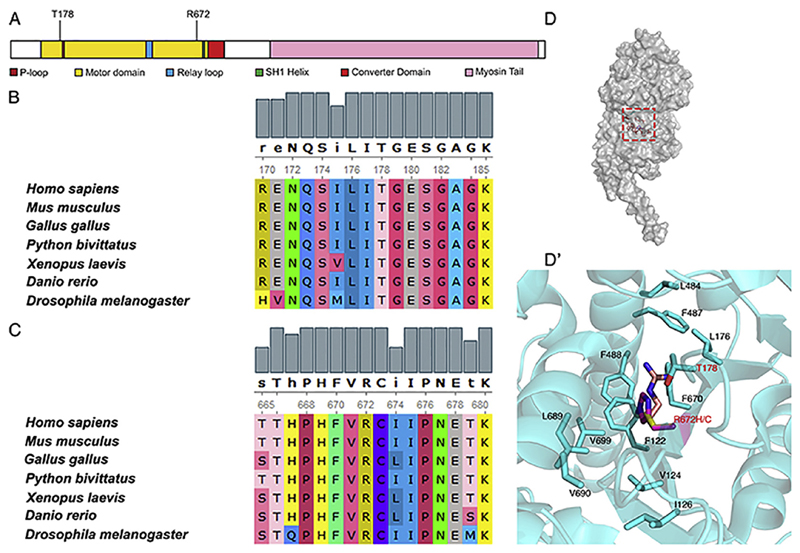
Fig. 1. The T178 and R672 residues in MyHC-embryonic which are mutated in FSS are evolutionarily conserved.
MyHC-embryonic protein schematic with the major protein domains and motifs labeled, showing the position of the T178 and R672 residues, which are the most frequently mutated residues in FSS (A). The T178 and R672 residues from human MyHC-embryonic were aligned to myosin heavy chain proteins from different vertebrate classes and the Drosophila myosin heavy chain using ClustalW (B, C). Both residues and neighboring residues are conserved across evolution (B, C). Surface representation of the monomer unit of Drosophila MHC (D). Magnified view of the boxed region in D showing the residues which are involved in hydrophobic packing in the ATP binding site of MHC (D′). Panel D and D′ are drawn in Pymol version 1.8 (PDB ID 5W1A). The R672 residue is mutated to H or C (R is light pink, C is yellow, and H is magenta).