FIG 1.
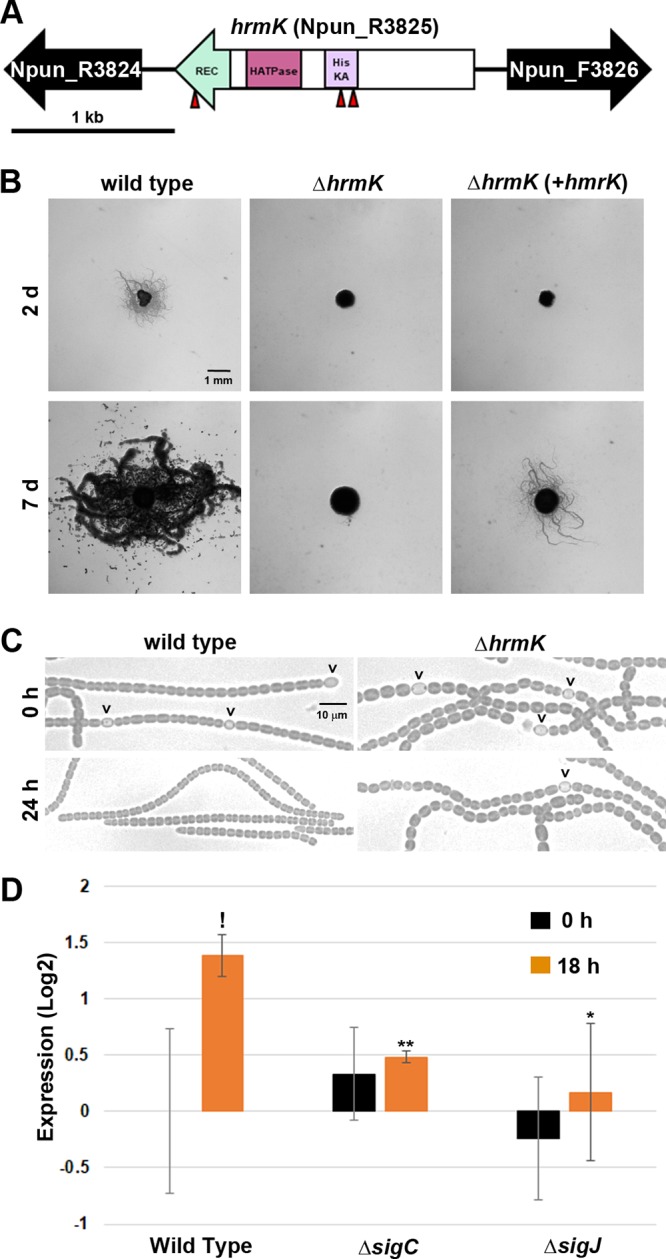
Characterization of hrmK. (A) Gene map of the hrmK locus. Triangles indicate the sites of transposon insertions. HisKA, His kinase A (phosphoacceptor) domain; HATPase, ATPase domains of histidine kinase; REC, response regulator receiver domain. (B) Plate motility assays of the wild-type strain, ΔhrmK mutant, and ΔhrmK mutant with hrmK expressed in trans from a shuttle vector (+hrmK) (as indicated). Images were taken at 2 days and 7 days postinduction. (C) Light micrographs of the filament morphology for the wild-type and ΔhrmK mutant strains (as indicated) at 0 h and 24 h post-hormogonium induction (as indicated). Carets indicate the presence of heterocysts attached to filaments. (D) RT-qPCR of hrmK in the wild-type, ΔsigJ mutant, and ΔsigC mutant strains 0 and 18 h after induction for hormogonia. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, as determined by two-tailed Student’s t test between the wild type and each deletion strain at the corresponding time point. !, P < 0.05; as determined by two-tailed Student’s t test between 0 and 18 h for the same strain.
