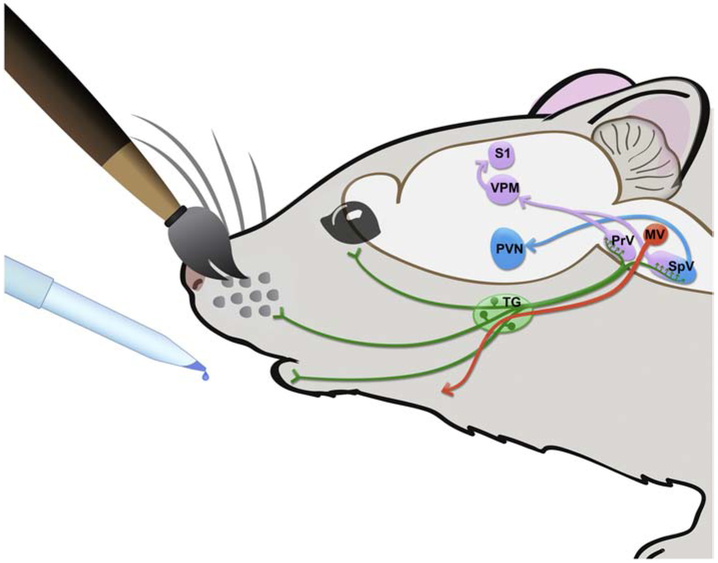
Figure 10: Illustration of experimental model:
Oxytocin receptor positive trigeminal sensory neurons (green) innervate the face. Ninety minutes after oral application of OXT or saline, with or without whisker brushing, c-Fos was measured in CNS regions of interest including the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN; blue), the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve (MV; orange), and the trigeminothalamocortical circuit (purple) carrying information about whisker stimulation (principal trigeminal nucleus, PrV; spinal trigeminal nucleus, SpV; ventroposterior medial nucleus of the thalamus, VPM; somatosensory neocortex in the barrel fields, S1). Anterograde circuit connections are emphasized in these regions of interest. Bidirectional circuitry exists (e.g. descending modulation of the brainstem by the hypothalamus), but it is not depicted in this schematic. Oral application of OXT, regardless of whisker brushing, reduced c-Fos density in the VPM thalamus of males and females and increased c-Fos density in the PVN of males. Oral application of OXT with whisker brushing reduced c-Fos density along the trigeminothalamocortical circuit (PrV, SpV, VPM, S1) of males and females and decreased c-Fos density in the trigeminal motor nucleus (MV) of females.