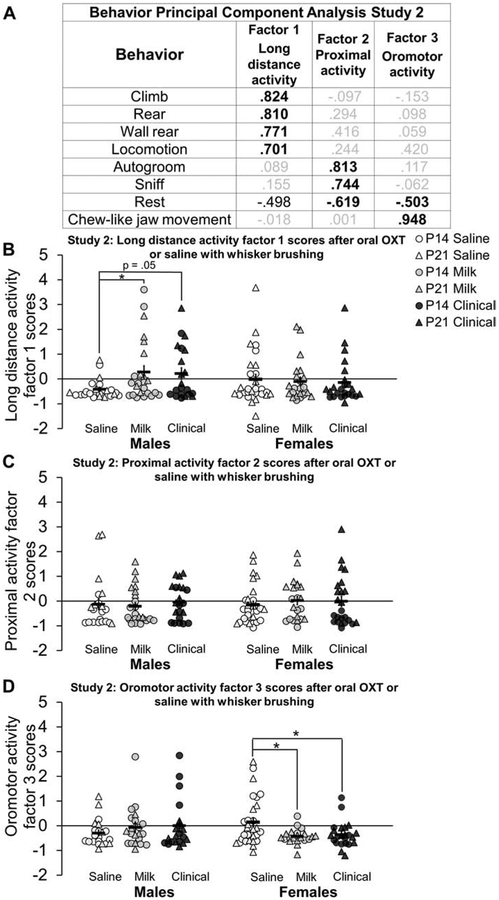
Figure 9: Oral oxytocin (OXT) with whisker brushing increases long distance activity factor 1 scores in males and decreases oromotor behavior factor 3 scores in females compared to saline:
Behavior principal component analysis and factor scores after a low dose (Milk; gray shapes) or high dose (Clinical; black shapes) of oral OXT or saline (white shapes) and whisker brushing in study 2 in postnatal day (P)14 (circles) and P21 (triangles) males and females in study 2. Behavior durations (in seconds) for ten minutes directly after oral OXT or saline administration with whisker brushing extracted three factors (A) reflecting long distance activity (factor 1), proximal activity (factor 2) and oromotor activity (factor 3). Bold black font emphasizes high loadings. Factor loadings were used to calculate behavioral factor regressions scores for long distance activity factor 1 (B), proximal activity factor 2 (C) and oromotor activity factor 3 (D). Clinical and Milk treated P14 and P21 males had higher long distance activity factor 1 scores compared to saline treated males, reflecting increased locomotor behavior (B). There were no differences between proximal activity factor 2 behavioral scores (C). Milk and Clinical treated P14 and P21 females had lower oromotor factor 3 scores compared to saline treated females, largely reflecting decreased chewing-like behavior (D). Individual data points are graphed ± SEM. *p = < 0.05.