Figure 4.
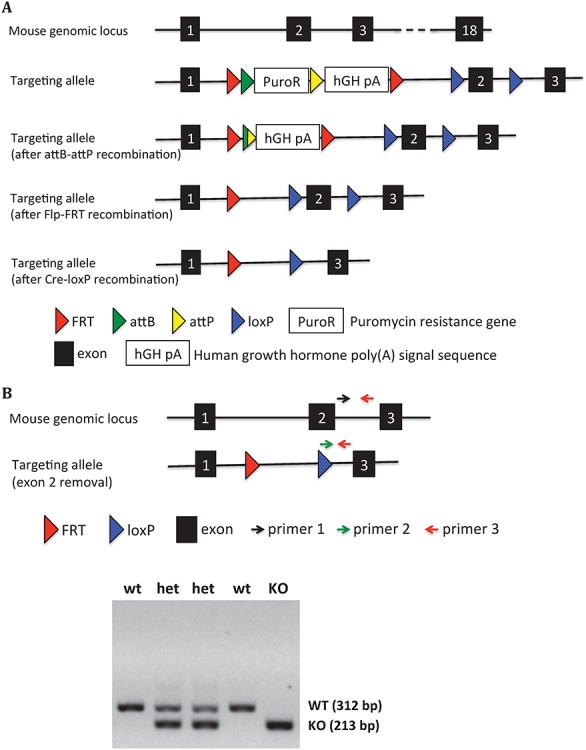
Generation of the Tmprss9 knockout mouse model. (A) The targeting vector was electroporated into ES cells, followed by injection into blastocysts that were implanted into pseudopregnant females. The puromycin resistance gene was removed by breeding with B6-Gt(ROSA)26SorphiC31, generating a constitutive knockout allele due to an insertion of a gene trap cassette between exon 1 and exon 2. The removal of human growth hormone poly(A) signal sequence was performed by breeding with C57BL/6-Tg(CAG-Flpe)2Arte mice, generating a conditional knockout allele. The removal of exon 2 was carried out by breeding with Hprttm1(CAG-cre)Mnn in B6 background, generating a second constitutive knockout allele. (B) Three primers (primer 1, 2 and 3) mixture in PCR reaction were used to genotype constitutive Tmprss9−/− mice (removal of exon 2). The size of WT allele and KO allele PCR products are 312 and 213 bp, respectively. (C) Semiquantitative PCR of Tmprss9 mRNA in Tmprss9−/− mice (removal of exon 2) in brains and kidneys using primers targeting exons 2–3. N = 2. Quantitative PCR of Tmprss9 mRNA in Tmprss9−/− mice (removal of exon 2) in brains and kidneys using primers targeting exons 5–6 (D) and exons 11–12 (E). N = 2.
