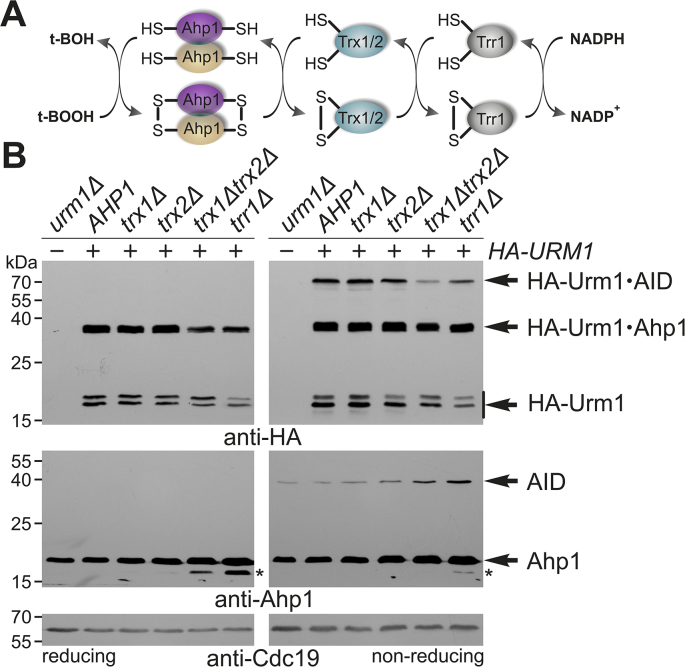
Fig. 2.
Thioredoxin function supports Ahp1 urmylation. (A) Ahp1 oxidation by ROS (t-BOOH) and reduction by the thioredoxin system, i.e. NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase (Trr1) and thioredoxins (Trx1; Trx2). (B) EMSAs under reducing (left panels) and non-reducing (right panels) conditions with protein extracts of indicated strains expressing HA-URM1 (+) or not (−). Urmylation was studied by anti-HA (top panels) diagnostic for free HA-Urm1 and urmylated forms of Ahp1 (~36 kDa) or Ahp1 intersubunit disulfides (AID ~72 kDa). anti-Ahp1 blots (middle panels) detect unmodified Ahp1 (~19 kDa) and AIDs (~38 kDa). anti-Cdc19 (bottom panels) served as loading control. Asterisks denote faster migrating Ahp1 forms.