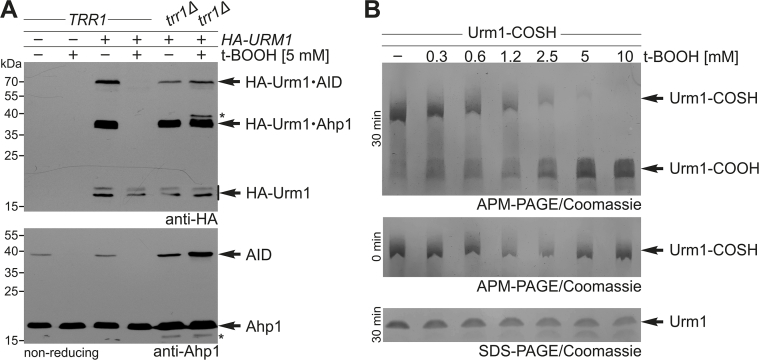
Fig. 4.
Effects of t-BOOH on Ahp1 reduction by thioredoxin and integrity of the thiocarboxylate of Urm1. (A) Inhibition of Ahp1 urmylation by t-BOOH relies on a functional thioredoxin reductase. EMSA under non-reducing conditions from TRR1 and trr1Δ cells expressing HA-URM1 (+) or not (−) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 5 mM t-BOOH. HA-Urm1 conjugation was studied by anti-HA Western blot (top panel) diagnostic for free HA-Urm1 and urmylated forms of Ahp1 (~36 kDa) and Ahp1 intersubunit disulfides (AID ~72 kDa). The anti-Ahp1 blot (bottom panel) detects unmodified Ahp1 (~19 kDa) and AID (~38 kDa). Asterisks denote faster Ahp1 forms (bottom panel) in trr1Δ cells and an unknown anti-HA signal (top panel). (B) t-BOOH exposure of Urm1 in vitro. Recombinant Urm1-COSH was treated with indicated t-BOOH doses and analyzed under non-reducing conditions by APM gel electrophoresis at time-point 0 min (middle panel) and 30 min (top panel) and under reducing SDS-PAGE conditions in the absence of APM after 30 min (bottom panel). Arrows distinguish the thiocarboxylate (Urm1-COSH) from the inactive form (Urm1-COOH).