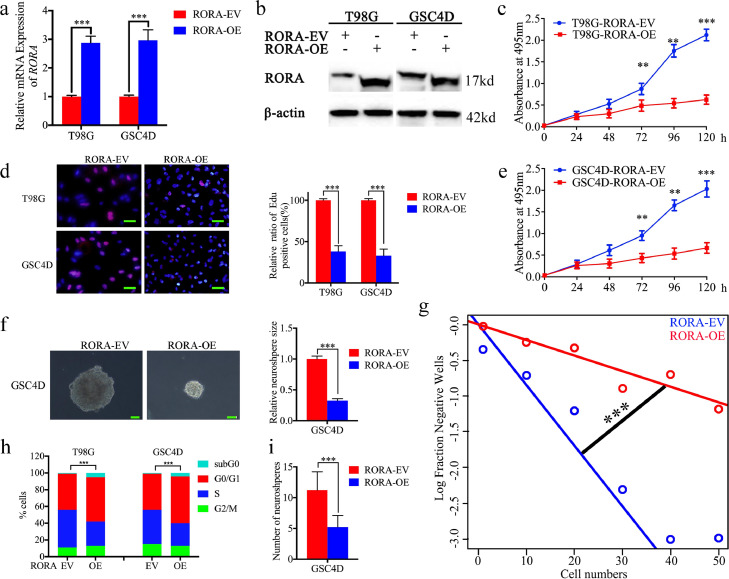
Fig. 2.
Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor A (RORA) overexpression inhibited glioma proliferation in vitro. (a) and (b) The lentiviral-based overexpression of RORA was detected by qPCR (a), T98G cells; P < 0.001; GSC4D; P< 0.001; Student's t-test) and western blots (b). (c) and (e) MTS assays showed the cell viability of T98G cells (c) P < 0.001; one-way analysis of variance and GSC4D (e) P < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance was decreased after RORA overexpression. (d) The Edu assay showed that the proliferations of T98G cells and GSC4D were decreased after RORA overexpression. (T98G cells: P < 0.001, GSC4D: P < 0.001; Student's t-test). Scale bar = 50 μm. (f) and (g) The neurosphere formation assay (f) and limiting dilution assays (g) showed the self-renewing capacity of GSC4D decreased after RORA overexpression (neurosphere size: P < 0.001, neurosphere number: P < 0.001; Student's t-test). Scale bar = 20 μm. (h) Cell cycle assay showed the effects of RORA on cell cycle distributions in T98G and GSC4D. (T98G cells: P < 0.001, GSC4D: P < 0.001; Student's t-test). All data are shown as the mean ± SD (from three independent experiments). *P < 0.05; ⁎⁎P < 0.01; ⁎⁎⁎P < 0.001.