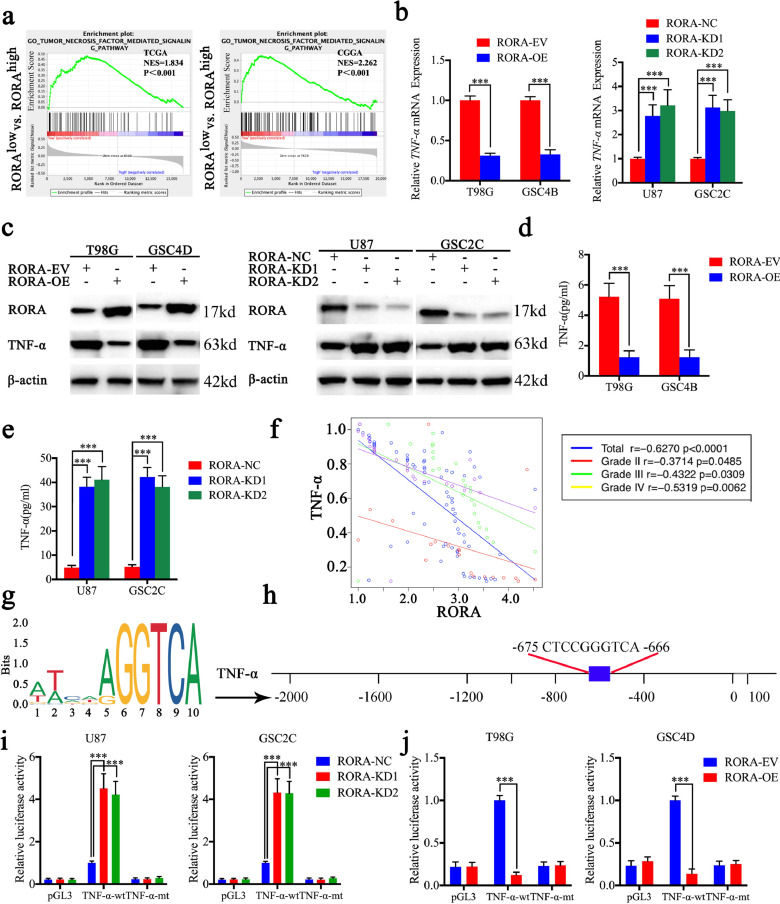
Fig. 3.
Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor A (RORA) inhibits the transcription and expression of TNF-α. (a) Gene set enrichment analysis indicated that high expression of RORA was negatively associated with the tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway in both TCGA and CGGA databases. (b)–(e) The expression and secretion of TNF-α after RORA overexpression or knockdown were detected by qPCR (b), RORA overexpression: T98G: P < 0.001, GSC4D: P < 0.001, Student's t-test; RORA knockdown: U87 cells: P < 0.001, GSC2C: P < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance, western blots (c) and ELISA (d) and (e). (f) The mRNA expression correlation between RORA and TNF-α in 70 cases of glioma patients were detected by qPCR. (g) Sequence motif representing the consensus RORA binding motif (JASPAR database). (h) Schematic representation of the human TNF-α promoter region. (i) and (j) RORA knockdown ((i), U87 cells: P < 0.001, GSC2C: P < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance) or overexpression ((j), T98G cells: P < 0.001, GSC4D: P < 0.001, Student's t-test) altered the luciferase promoter activities of TNF-α. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD (from three independent experiments). *P < 0.05; ⁎⁎P < 0.01; ⁎⁎⁎P < 0.001.