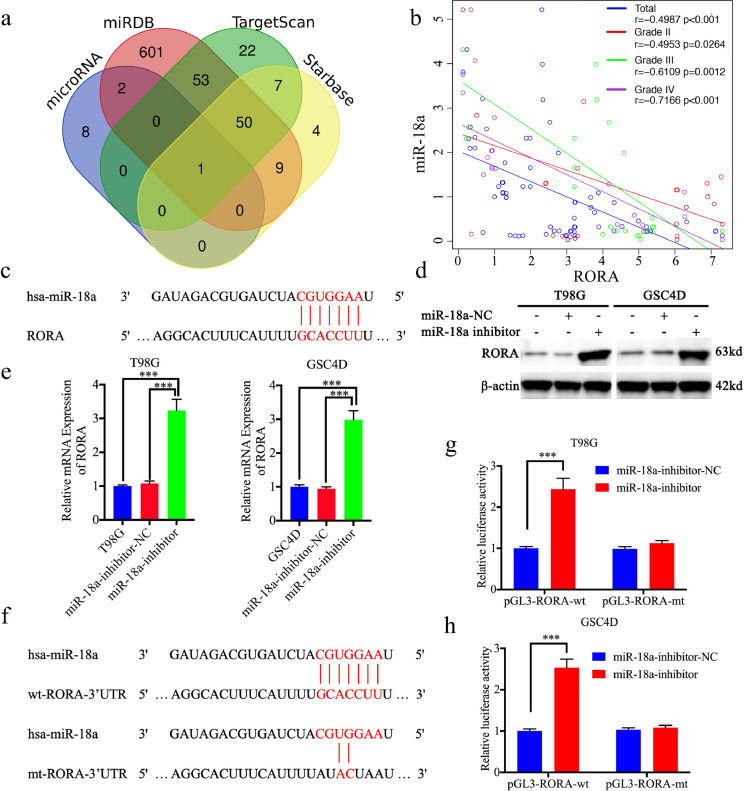
Fig. 6.
miR-18a negatively regulated retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor A (RORA) expression by binding with the RORA 3′-UTR. (a) Identification of a miRNA that potentially regulated RORA expression based on Starbase, TargetScan, microRNA, and miRDB. (b) The mRNA expression correlation between RORA and miR-18a in 70 cases of glioma patients were detected by qPCR (r = −0.4987, P < 0.001, Pearson's correlation analysis). (c) and (f) Schematic diagram of the putative miR-18a binding site in the 3′-UTR of RORA in humans. (d) and (e) Western blotting (d) and qPCR (e) showed the expression of RORA increased after miR-18a inhibitor treatment (T98G cells: P < 0.001; GSC4D: P < 0.001, Student's t-test). (g) and (h) MiR-18a inhibitor treatment increased the luciferase promoter activities of RORA ((g), T98G cells: P < 0.001; (h), GSC4D: P < 0.001, Student's t-test). All data are shown as the mean ± SD (from three independent experiments). *P < 0.05; ⁎⁎P < 0.01; ⁎⁎⁎P < 0.001.