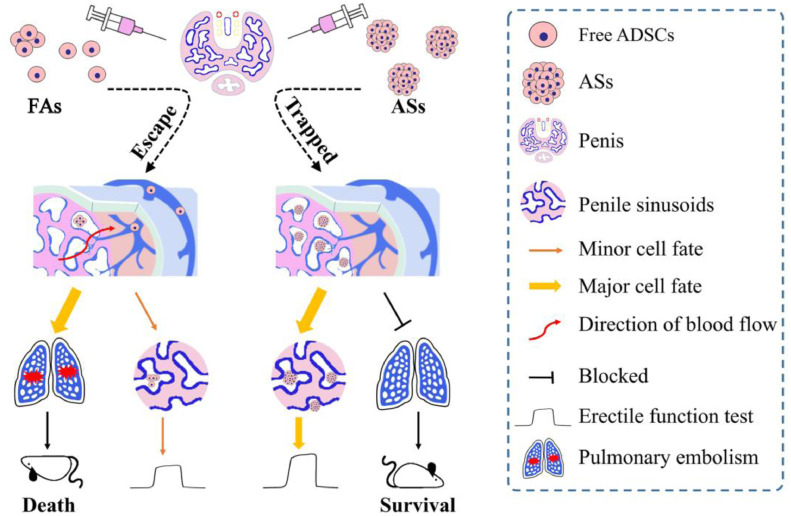
Fig. 7.
Schematic illustrating the efficacy and safety of FAs and size-specific ASs for ED therapy through ICI. The cavernous sinusoidal structure made it easy for free cells to escape from CC, leading to reduced therapeutic efficacy for ED and high risk of pulmonary embolism. Conversely, formation of size-specific ASs, whose sizes could be controlled by adjusting cell numbers, is an efficient method to trap stem cells in CC, to improve therapeutic efficacy and to avoid pulmonary embolism.