Figure 5.
Clonal Diversification Is Uncoupled from Selection Forces in PP GCs
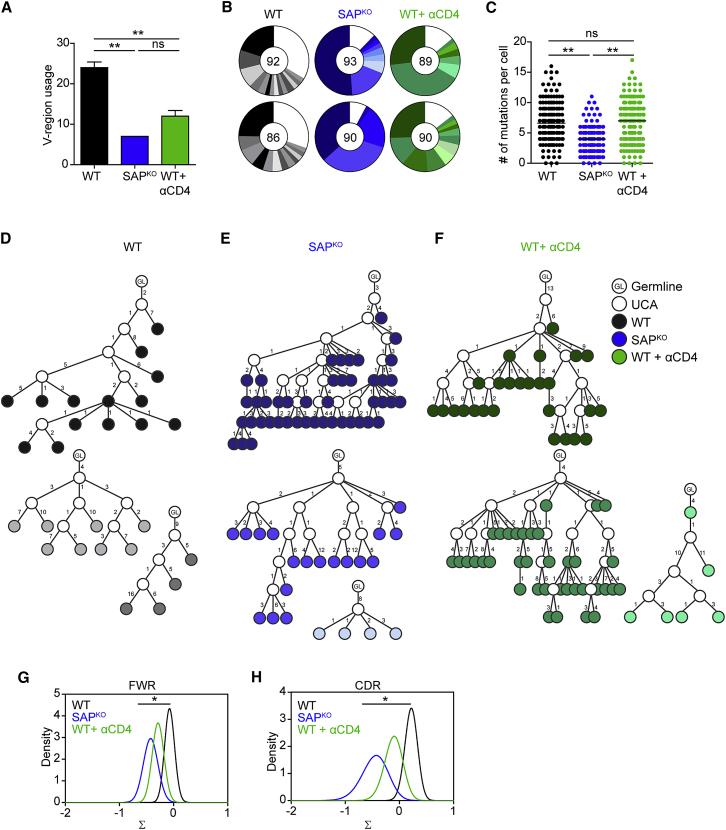
(A) The number of V-regions detected in IgA sequences of GC-derived (GL7+ FAS+ IgA+) B cells recovered from a single PP derived from either WT, SAPKO, or WT mice treated with αCD4-depleting antibody for 14 days (WT + αCD4).
(B) Clonal distribution based on CDR3 sequences, as in (A). Colored fractions represent expanded CDR3 sequences (>2); white fraction represents single clones. Each pie chart represents one mouse (n = 2). The number of sequenced cells is indicated in the center circle.
(C) Number of mutations per B cell of the cells described in (A). Data are pooled from two independent experiments with one mouse in each experiment. ∗∗p < 0.01, one way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest. ns, not significant.
(D–F) Lineage-tree analysis of clonally related sequences in WT (D), SAPKO (E), and WT + αCD4 (F) GC B cells. The number of mutations between neighboring nodes is indicated and includes synonymous, non-synonymous, and reverse mutations to the germline sequence. GL, germline; UCA, unique common ancestor, inferred from the sequence analysis.
(G and H) Graphs showing the density of selection strength for all analyzed sequences within the framework (FWR) (G) or complementary determining region (CDR) (H) of WT, SAPKO, and αCD4 treated mice. Selection was estimated using BASELINe focused test with the RS5NF mutability model. ∗False discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05.