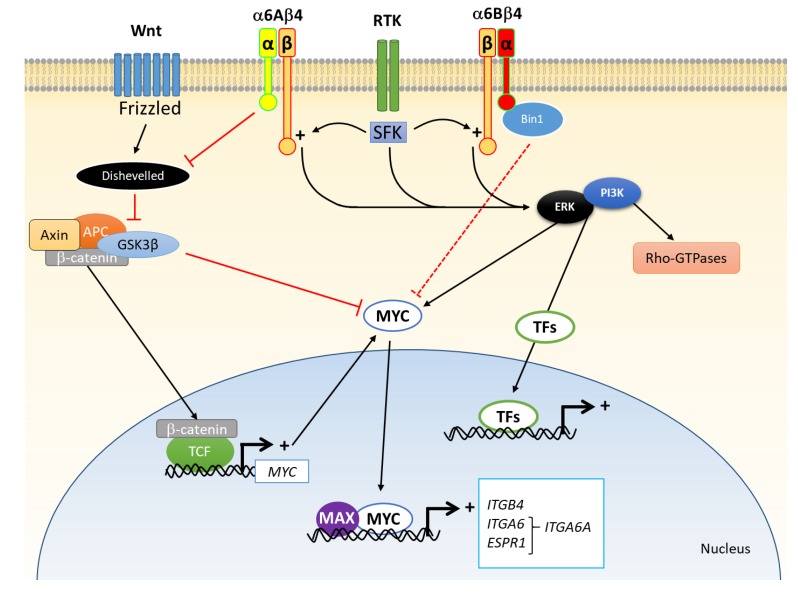
Figure 2.
Some of the signaling pathways regulated by integrin α6β4 in colorectal cancer cells. First is the cooperation between receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK), which via Src family of kinases (SFK) trigger phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of β4 to activate the ERK and PI3K signaling pathways, which in turn regulate various cellular functions such as migration, proliferation and survival by the modulation of specific transcription factors (TFs) and activation of the Rho-GTPases. Second are the regulatory effects of the α6 subunit on cell proliferation where α6A promotes the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and the expression of downstream effectors such as MYC while α6B appears to inhibit MYC activity by a possible interaction with the protein bridging integrator 1 (Bin1). MYC appears also as one key regulator of integrin expression since both ITGB4 and ITGA6 have MYC-responsive elements in their promoters as for ESPR1 that encodes a splicing factor that regulate ITGA6A expression. Adapted from [18,36,39,40].