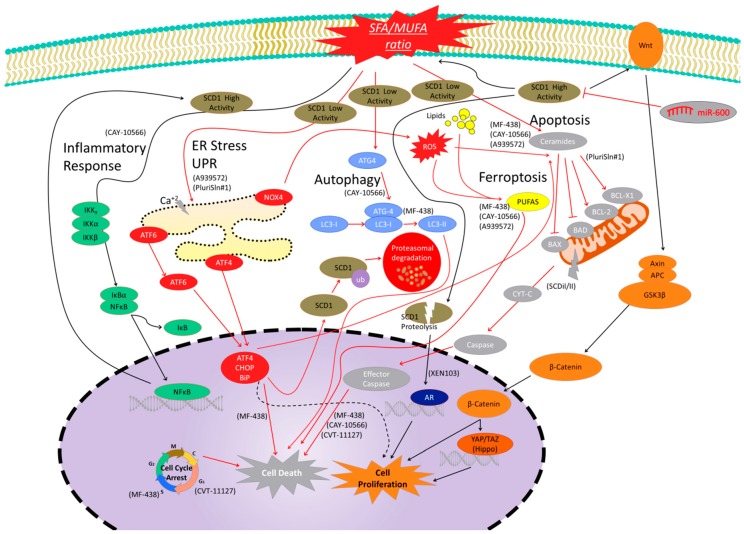
Figure 2.
Signaling pathways modulated by SCD1 activity and levels. Black arrows are signals of cell proliferation or associated with high SCD1 expression or activity, while red arrows are signals linked to cell death or decreased SCD1 expression or activity. Inflammatory pathway is shown in green. SCD1 inhibition reduces the pro-inflammatory environment and nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) signaling to reduce cell proliferation, while NFκB signaling activation promotes transcription factors binding to SCD1 promotor and gene expression. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is related to cell proliferation and it is shown in orange. High SCD1 levels are linked to increased β-catenin signaling and increased levels of wingless-related integration site (Wnt) ligands to induce cell proliferation. Hippo pathway is a β-catenin-related signal cascade, which is associated with cell proliferation, and SCD1 inhibition has been demonstrated to be associated with decreased levels of Hippo target genes. This pathway is shown in dark orange. The SCD1 peptides from proteolytic controlled degradation activate androgen receptor (AR) signaling to promote cell proliferation. This pathway is shown in dark blue. The autophagy cell death pathway is a protein cascade which is upregulated after SCD1 inhibition. Some central elements of this pathway are shown in light blue. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signal pathway is shown in red. This cascade is linked to misfolded and unfolded proteins to induced cell death. SCD1 inhibition has been linked to the upregulation of the elements of the ER pathway to promote cell death. SCD1 is also ubiquitinated by this pathway to promote protein degradation. However, light ER pathway activation has also been related to cell survival (dashed black arrows). Apoptosis is a programmed cell death shown in grey that is activated after SCD1 inhibitor treatments. Increased ceramides, mitochondrial effector pathway, caspases, and other pathway effectors have been detected after treatments. Ferroptosis is another cell death mechanism (yellow) that has been shown to be activated after SCD1 Inhibition. Finally, SCD1 inhibition has been demonstrated to induce cell cycle arrest in different checkpoints to promote cell death. Molecules in parentheses are SCD1 inhibitors used in the literature to elucidate the SCD1-related pathways.