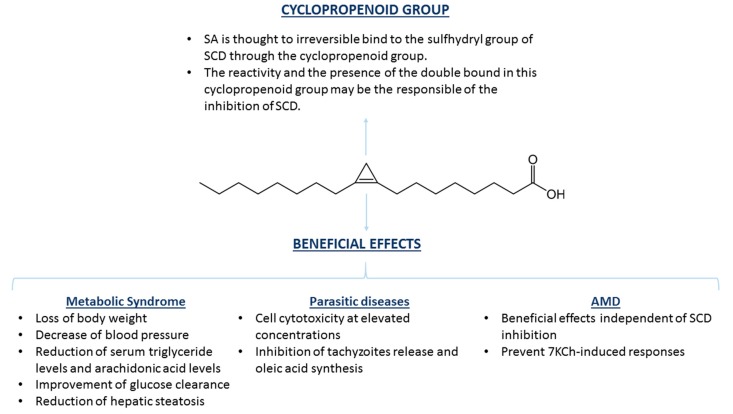
Figure 3.
Chemical structure of SA and beneficial effects exerted in several pathologies. The cyclopropene group of SA has been suggested to be responsible for both binding and inhibition of SCD as a consequence of the reactivity of the double bond between C9 and C10. Inhibition of SCD by SA has been described as potentially therapeutic for several diseases, such as those related with metabolic syndrome and parasitic diseases. Positive effects of SA have also been shown in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), although the effects seem to be independent of SCD inhibition.