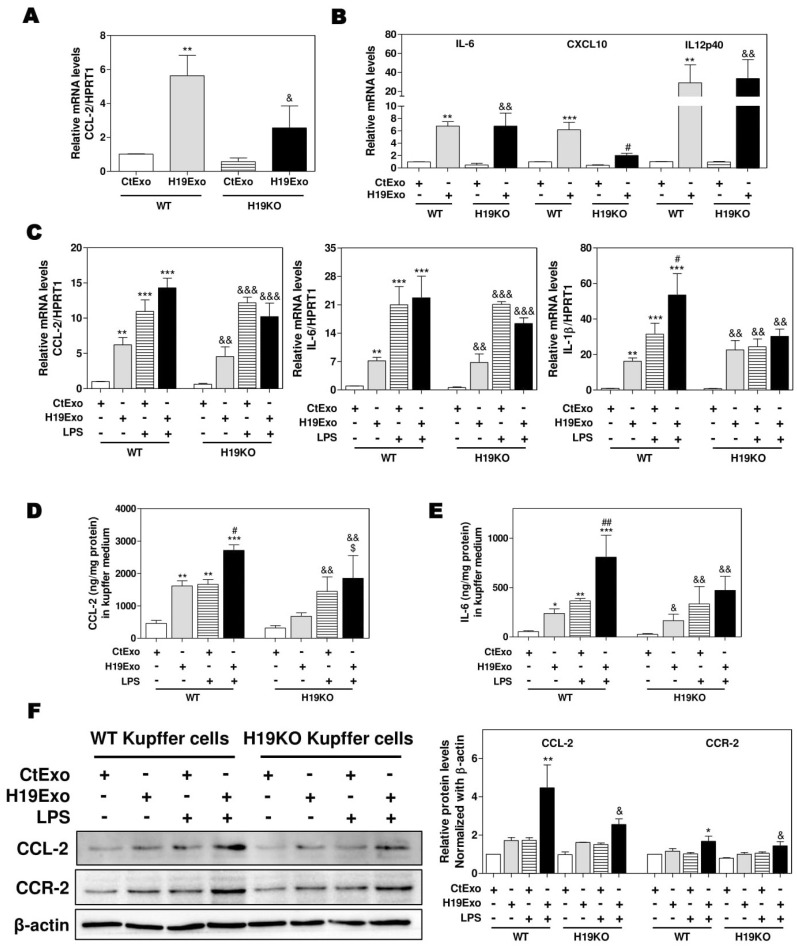
Figure 1.
Cholangiocyte-derived exosomal H19 promotes Kupffer activation. (A,B) Mouse Kupffer cells were treated with control mouse large cholangiocytes (MLE)-derived exosomes (CtExo) and H19-overexpressing MLE-derived exosomes (H19Exo) for 24 h. (A,B) The relative mRNA levels of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL-2), interleukin-6 (IL-6), chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 (CXCL10), and IL12p40 were measured by real-time RT-PCR and normalized using HPRT1 (Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase 1). (C–F) Mouse Kupffer cells were treated with CtExo, H19Exo, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (10 ng/mL) for 24 h. (C) The relative mRNA levels of CCL-2, IL-6, and IL-1β were measured by real-time RT-PCR and normalized using HPRT1. (D,E) The protein levels of CCL-2 and IL-6 in the conditioned medium of Kupffer cells were measured by ELISA assay and normalized using protein concentration. (F) Representative immune blot images of CCL-2 and CCR-2 are shown. Relative protein levels were normalized using β-actin. Results from at least three independent experiments are presented as Mean ± SEM. Statistical significance: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with WT control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, compared with WT H19Exo group; & p < 0.05, && p < 0.01, &&& p < 0.001, compared with H19KO control group; $ p < 0.05, compared with H19KO H19Exo group.