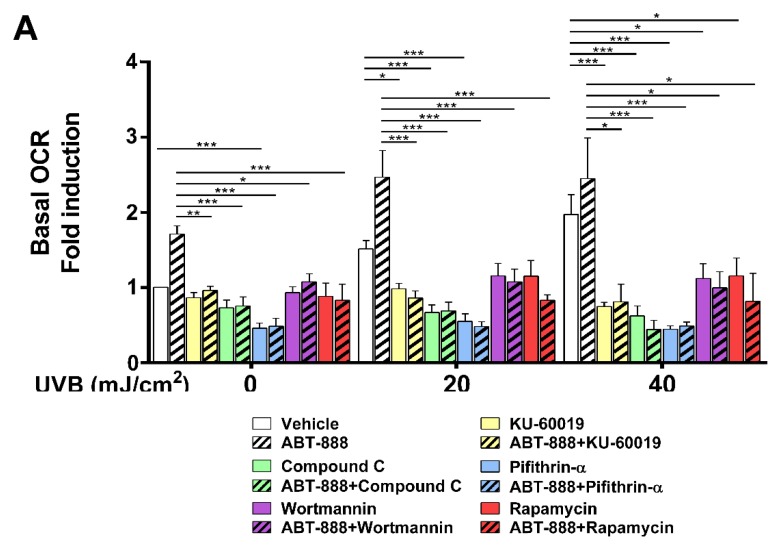
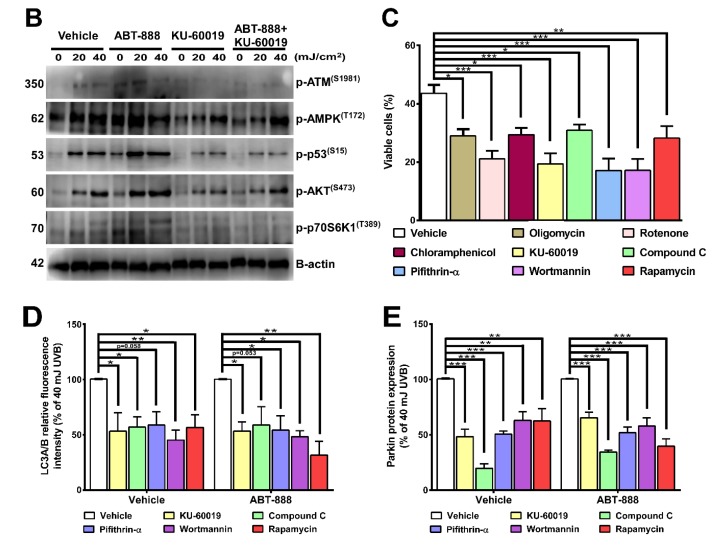
Figure 9.
PARP inhibition and UVB-induced oxidative phosphorylation and autophagy are dependent on ATM, AMPK, p53, AKT, and mTOR activation. (A) To determine key proteins involved in mediating mitochondrial changes ATMi (KU-60019), AMPKi (Compound C), p53i (Pifithrin-alpha-HBr), PI3Ki (Wortmannin), and mTORi (Rapamycin) were added to the medium and OCR was measured as in Figure 6C (n = min.3). (B) ATM downstream signaling pathway was investigated by Western blot with the addition of its pharmacological inhibitors KU-60019 (n = 3). Brightness and contrast were adjusted. (C) Cell viability was measured by flow cytometry as in Figure 1E after 40 mJ/cm2 UVB with oligomycin, rotenone, chloramphenicol, ATMi, AMPKi, p53i, PI3Ki, and mTORi (n = min. 4). To determine the involvement of ATM, AMPK, p53, AKT, and mTOR in the regulation of (D) autophagy and (E) PARKIN expression, we applied their respective pharmacological inhibitors after 40 mJ/cm2 UVB. (n = 4). *; ** and *** indicate statistically significant difference at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, p < 0.001, respectively. Error bars represent SEM. ATM: ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated kinase, AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase, AKT: protein kinase B, mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin, OCR: oxygen consumption rate.