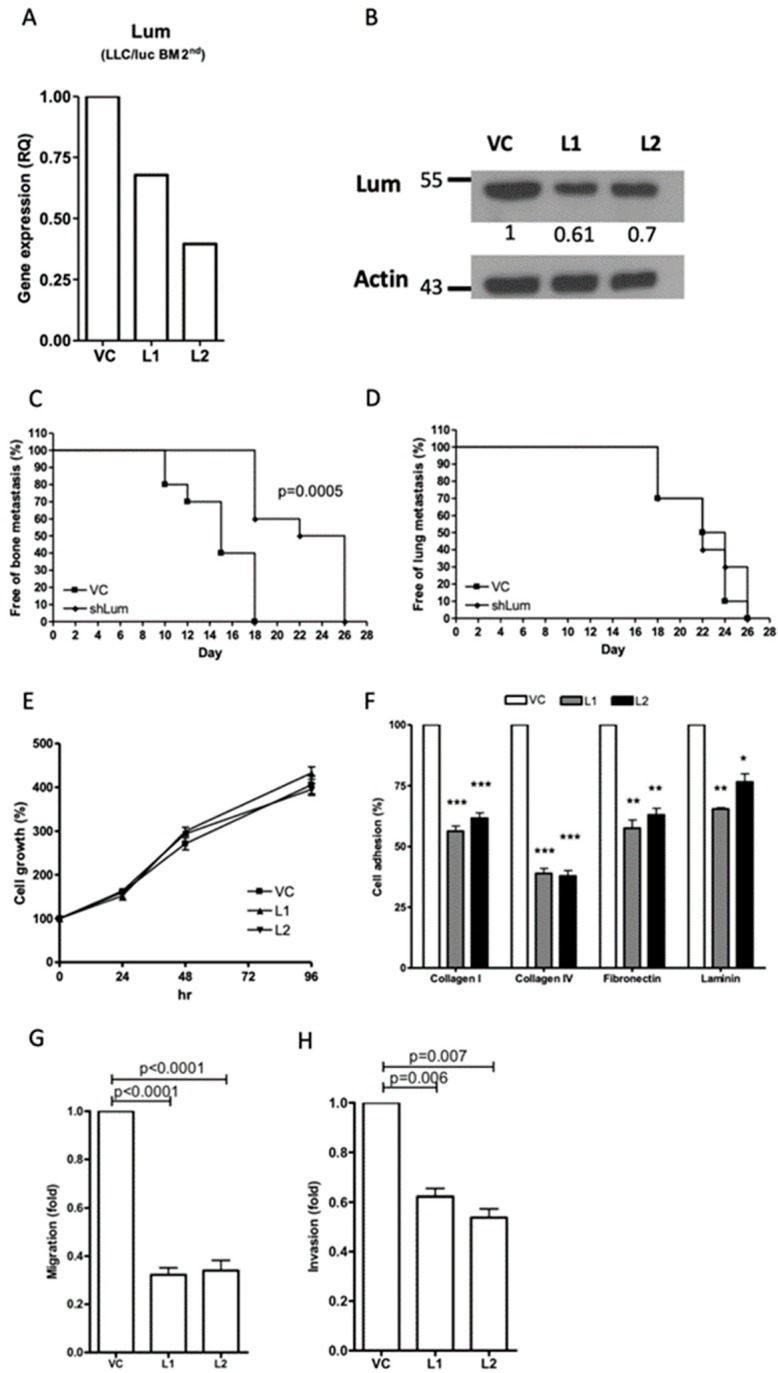
Figure 2.
Effect of lumican knockdown on the function of bone metastatic LLC/luc BM 2nd cells. The expression of lumican in LLC/luc BM 2nd cells transfected with a control vector (VC) and a lumican-specific short hairpin RNA (shRNA) plasmid (L1 and L2) was determined by real-time RT-PCR (A) and Western blot analysis (B). The level of lumican expression in each cell was individually normalized to the internal control (actin), and the numbers in (B) indicate the level of lumican expression in lumican knockdown LLC/luc BM 2nd cells as compared to that in the cells transfected with the control vector. The LLC/luc BM 2nd cells transfected with a control vector (VC) and a lumican-specific shRNA (shLum) were administered by injecting them intracardiac (I.C.) and intravenous (I.V.) to allow the establishment of bone (C) and lung (D) metastasis (n = 10, from two separate experiments), respectively. The presence of tumor metastasis as determined by the presence of luciferase activity was detected by the IVIS imaging system. The cell proliferation (E) and adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) components (F) of LLC/luc BM 2nd cells transfected with the control vector (VC) and the lumican-specific shRNA plasmid (L1, L2) were determined by an Methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and a cell adhesion assay, respectively. The migration (G) and invasion (H) abilities of LLC/luc BM 2nd cells transfected with the control vector and the lumican-specific shRNA plasmid were determined by the Transwell migration assay. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, and *** p ≤ 0.001. The error bars are defined as means ± SEM.