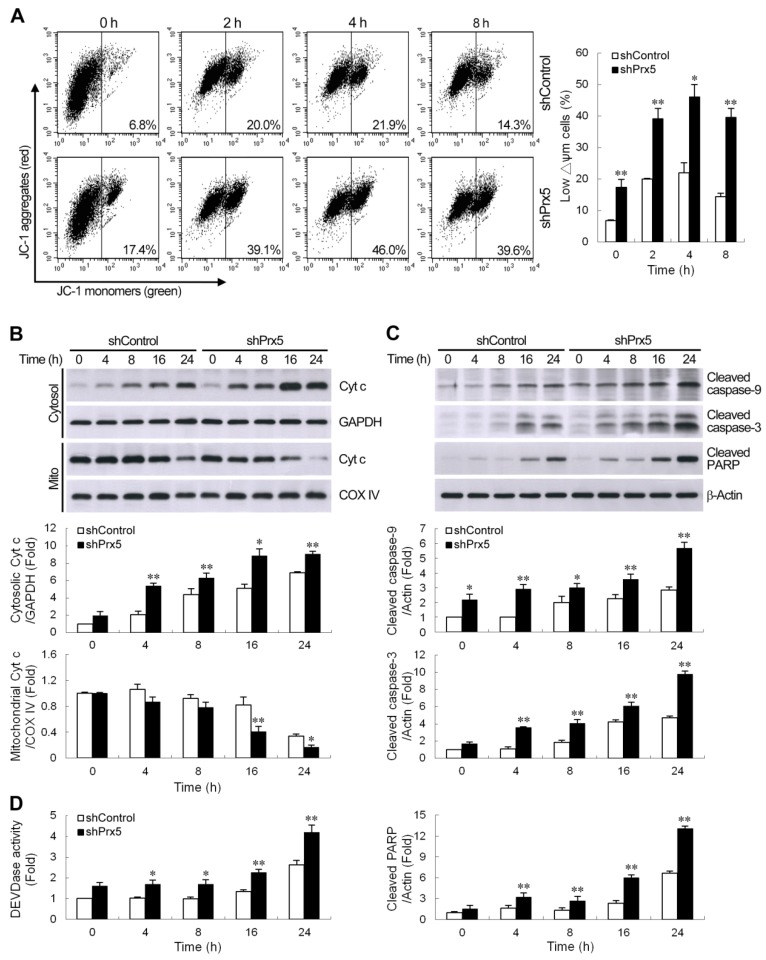
Figure 3.
The knockdown of Prx5 exacerbated mitochondria-mediated apoptotic signaling by rotenone. (A) Control and Prx5-depleted cells were cultured with rotenone (10 μM) for the indicated times, and changes in mitochondrial membrane potential were then evaluated by staining with JC-1 (5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-benzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide). Representative histograms of flow cytometry analysis of JC-1 staining are shown (left panels). The right panel shows the percentage of cells with a low Δψm (increased green fluorescence of the JC-1 monomer). (B) Cells were exposed to rotenone (10 μM) for the indicated times. Cytochrome c protein levels were assessed in cytosolic and mitochondrial (Mito) fractions by western blot analysis. Immunoblots for GAPDH and COX IV are shown for normalization of cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions, respectively. (C,D) After exposure to rotenone, whole-cell lysates were prepared, and the activation of caspases cascade was determined by western blotting (C). The graphs show the quantification analysis of cleaved caspase-9, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)/β-actin. Caspase-3-like protease activity (D) in cell lysates was also measured by cleavage of the fluorogenic substrate Ac-DEVD-AMC. Caspase-3-like activity from the non-stimulated control shRNA-expressing cells was arbitrarily set at 1 for the calculation of fold. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3–4 independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 compared with respective control shRNA-expressing cells.