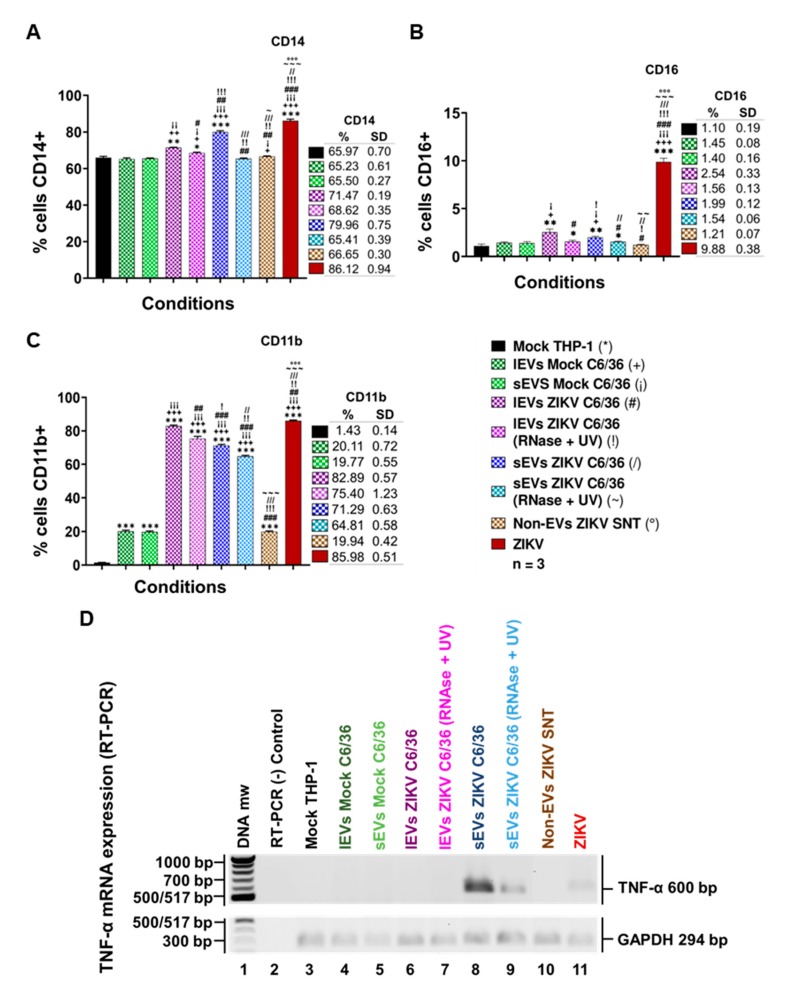
Figure 8.
EVs from ZIKV-infected C6/36 favor the pro-inflammatory phenotype change in naïve human monocytes. (A) Monocytes CD14+ percentages (FACS) at different EV stimuli conditions from three independent experiments. (B) Monocytes CD16+ percentages (FACS) at different EVs stimuli conditions from three independent experiments. (C) Monocytes CD11b+ percentages (FACS) at different EVs stimuli conditions from three independent experiments. The CD14, CD16, or CD11b levels were compared (by an unpaired Student’s t-test) between all conditions’ values. Statistical significance was recognized as *, +, ¡, #, !,/, ~, or ° when p < 0.05, **, ++, ¡¡, ##, !!,//, ~~, or °° when p < 0.01, and ***, +++, ¡¡¡, ###, !!!,///, ~~~, or °°° when p < 0.0001. (D) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) mRNA expression (RT-PCR) in naïve monocytes at different EVs stimuli conditions. The TNF-α genome conserved region (amplicon of 600 bp) was visualized on 2% ethidium bromide-stained 1.2% agarose gel.