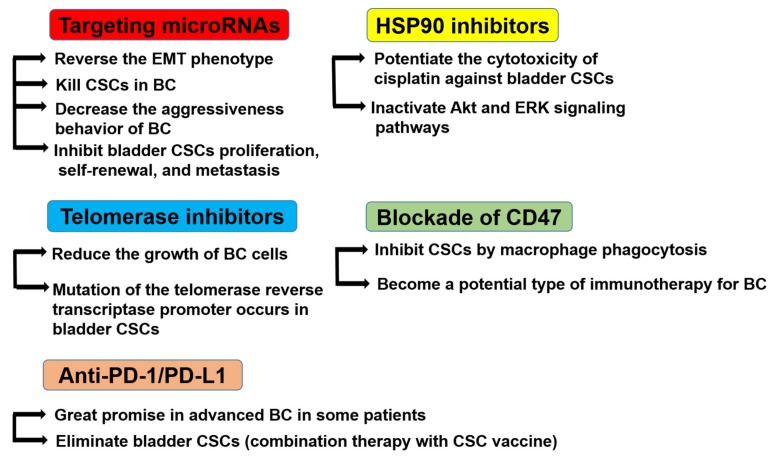
Figure 4.
Potential therapeutic targets for bladder CSCs. Targeting microRNAs reverses the EMT phenotype, kills CSCs in BC, decreases the aggressiveness behavior of BC, and inhibits bladder CSC proliferation, self-renewal, and metastasis. HSP90 inhibitors potentiate the cytotoxicity of cisplatin against bladder CSCs and inactivate the Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Telomerase inhibitors reduce the growth of BC cells, and the mutation of the telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter occurs in bladder CSCs. The blockade of CD47 inhibits CSCs by macrophage phagocytosis and may become a potential type of immunotherapy for BC. Anti-programmed cell death (PD)-1/ programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) therapy has shown great promise in advanced BC in certain patients. The combination therapy of PD-1 blockade and CSC vaccine therapy could eliminate bladder CSCs.