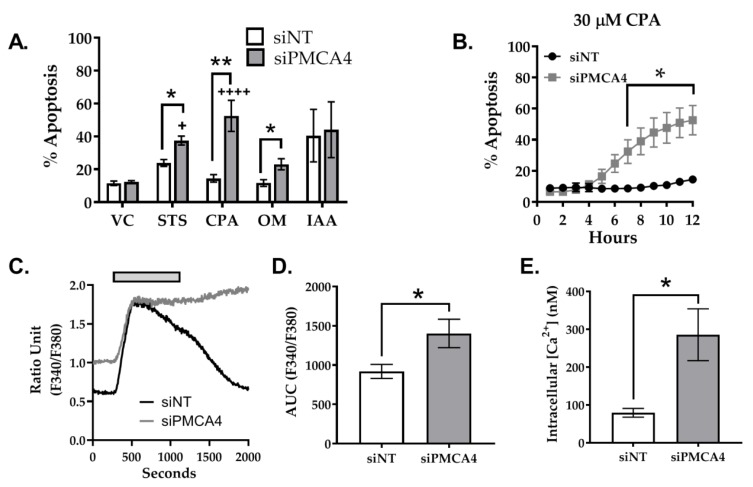
Figure 6.
PMCA4 knockdown enhances apoptosis associated with Ca2+ overload. MIA PaCa-2 cells were seeded in either non-targeting control (siNT) or siRNA targeting PMCA4 (siPMCA4) for 48 h then treated with either 0.1% DMSO vehicle control (VC), apoptotic-inducing staurosporin (STS), cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), oligomycin (OM) or iodoacetate (IAA). The cells were labelled with Nuclear-ID red stain and caspase3/7 reagent prior to imaging using the Incucyte® live-cell analysis system. (A) Cell death is shown as the percentage of caspase 3/7 cleavage with respect to total cell count post-12-hour treatment. (B) The effects of CPA-induced apoptosis was further examined at 0.5–12 hr. (C) Ca2+ overload assay was used to examine the relationship between CPA and Ca2+ overload-associated cell death. Fura-2 loaded cells were perfused with HPSS for 200 seconds. After baseline signals were stable, cells were perfused with 30 µM CPA added HPSS (grey box) for 15 minutes and were washed with HPSS for 15 minutes. Representative Ca2+ overload traces of siNT control (black) and siPMCA4 (grey) are shown. (D) Baseline-subtracted mean area under the curve (AUC) of the uncalibrated fura-2 fluorescence ratios and (E) calibrated resting [Ca2+]i for siNT vs. siPMCA4 treated cells are shown. Statistical significance comparisons between siNT and siPMCA4 treated conditions were determined by Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. (N = 3–5 experiments; 3 replicates per treatment condition) * and ** represent statistically significant differences between siNT vs. siPMCA4 where p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively. + and ++++ represent statistically significant differences between VC vs. treatment conditions where p < 0.05 and p < 0.0001, respectively.