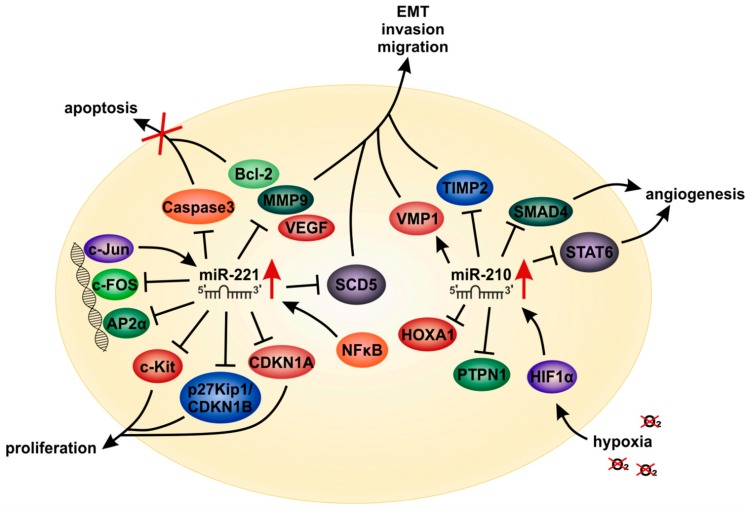
Figure 7.
OncomiRs miR-221 and miR-210 and their impact on cancer cells. The miRNAs miR-221 and miR-210 are significantly upregulated during tumor development of melanoma and HCC (indicated by red arrows) which leads to interference with important cellular pathways. MiR-221 downregulates the transcription factors c-FOS [196] and AP2α [191] and is regulated itself by c-Jun and the NFκB pathway [213]. NFκB regulation also leads to suppression of the miR-221 downstream genes Bcl-2, VEGF and MMP-9 thus inhibiting apoptosis [196]. MiR-221-associated anti-apoptotic activity is further mediated by targeting caspase-3 [209]. Regulation of Bcl-2, VEGF and MMP-9 by miR-221 can also induce an invasive phenotype which is further mediated by miR-221 suppressing SCD5 and thereby promoting EMT [193]. Additional miR-221 targets are c-Kit, p27Kip1/CDKN1B and CDKN1A whose downregulation in cancer induces cell proliferation [194,195,212]. MiR-210 can also influence EMT and migration via inhibition of TIMP2 [215] and activation of VMP1 [216]. Downregulation of SMAD4 and STAT6 by miR-210 promotes angiogenesis [217]. Further important targets of miR-210 in tumor cells are HOX1A and PTPN1 interfering with the immune response [218]. MiR-210 expression is induced during hypoxia [219,220] through regulation by HIF1α [221].