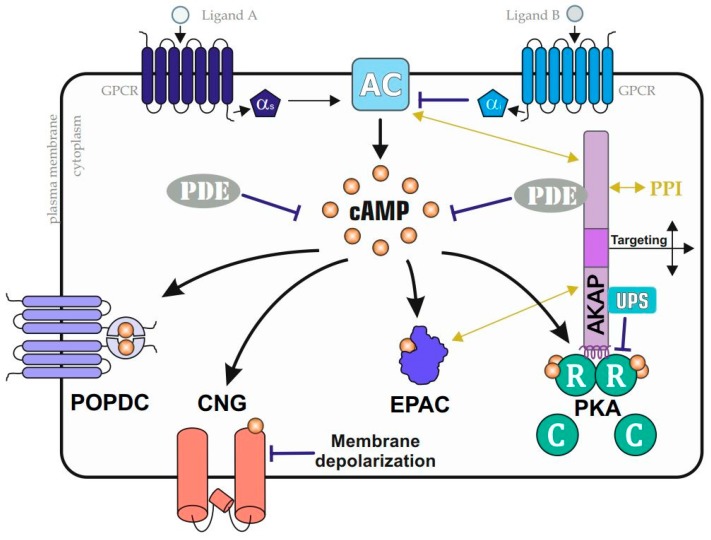
Figure 2.
Prominent cAMP–effector pathways. A collection of GPCRs modulates adenylyl cyclase (AC) activities. AC stimulating or inactivating G alpha proteins (Gαs or Gαi, respectively) control cAMP accumulation, which is sensed by a collection of indicated cAMP-binders. In addition to cytoplasmic cAMP-dependent exchange protein (Epac) and protein kinase A (PKA) complexes, membrane-bound cyclic nucleotide-gated ion (CNG) channels and Popeye domain-containing proteins (POPDC) proteins sense cAMP fluxes. PKA is compartmentalized by A kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs), which coordinate the formation of cell- and context-specific subcellular PKA nanodomains through functional interactions with phosphodiesterases (PDEs); the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS); and/or through additional PPIs (with, for example, ACs and Epacs), which are AKAP and nanodomain specific (indicated by the yellow arrows).