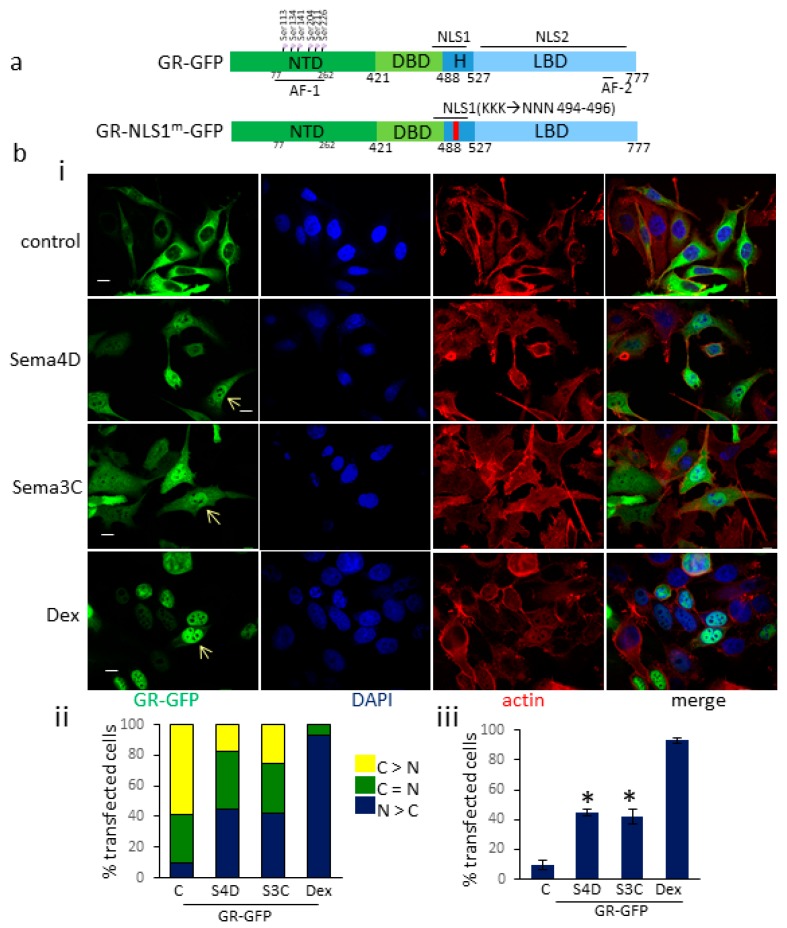
Figure 2.
PlexinB1 activation promotes translocation of GR-GFP to the nucleus. (a). Diagram to show structure of GR constructs used. NTD: N-terminal domain, DBD: DNA binding domain, H: hinge region, LBD: ligand binding domain, NLS: nuclear localisation sequence. (b). (i). Representative images of PC3 cells transfected with GR-GFP and treated with Sema4D (2 μg/mL), Sema3C (2 μg/mL), dexamethasone (10 nM) or vehicle (control) for 60 min. The cells were fixed and stained for actin (phalloidin-TRITC) and DNA (DAPI). Arrow denotes nuclear GR-GFP. Scale bar, 10 μm. (ii). Subcellular localisation of GR-GFP in transfected PC3 cells. Following treatment with Sema4D (2 μg/mL), Sema3C (2 μg/mL), dexamethasone (10 nM) or vehicle (control) for 60 min, PC3 cells transfected with GR-GFP were stained as in (i) and were scored blind and categorised into three groups: (1) nuclear GFP staining > cytoplasmic GFP staining (N > C), (2) nuclear and cytoplasmic GFP staining equal, (n = C), (3) cytoplasmic GFP staining > nuclear GFP staining (C > N) and the % of cells in each group scored (n = 3). A total of 175+ cells were scored per treatment. (iii) Percentage of cells transfected with GR-GFP in which the intensity of nuclear GFP staining exceeded that of cytoplasmic staining (N > C) following treatment with Sema4D (2 μg/mL), Sema3C (2 μg/mL), dexamethasone (10 nM) or vehicle (control, C) for 60 min (n = 3). Error bars denote SEM, * p < 0.05, Ttest).