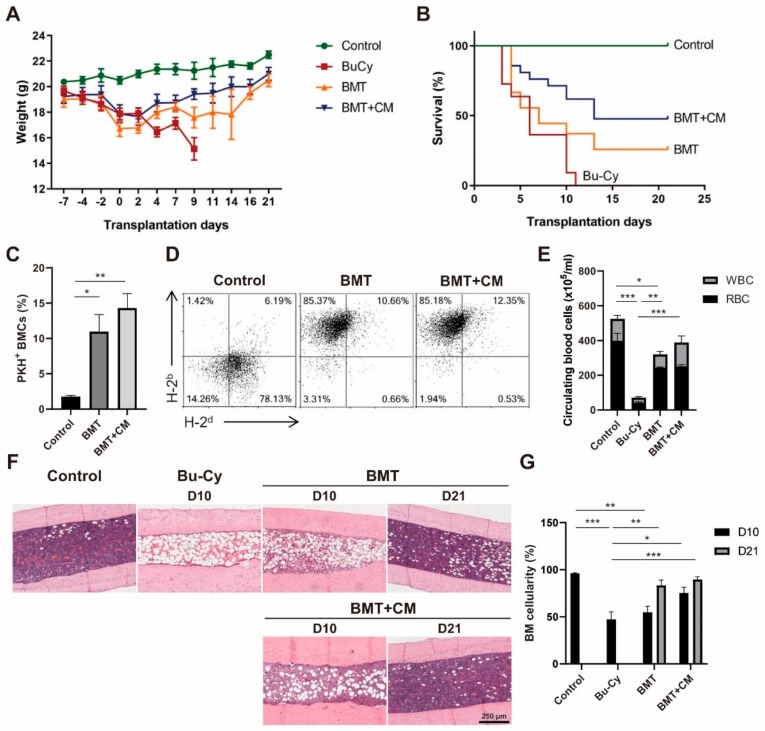
Figure 1.
T-MSC CM treatment promotes BM reconstitution after BMT. BMT was performed in mice preconditioned with Bu–Cy administration with or without T-MSC CM. (A) Mouse body weight was measured throughout the course of experiments. (B) Survival rate was determined using Kaplan–Meier estimates. (C) PKH26-labeled donor cells were detected in mouse femurs on day 4 post-BMT using flow cytometry. (D) Analyses of MHC haplotype expression of blood mononuclear cells were conducted on day 10 post-BMT using flow cytometry. H-2b represents the donor C57BL/6 cells and H-2d for BALB/c recipient. (E) The numbers of RBCs and WBCs in peripheral blood were examined using a Coulter counter cell-sizing analyzer on day 10 post-BMT. (F) Histological analysis of BM cellularity was performed on day 10 and 21 post-BMT, and representative images of H&E staining from mouse femurs are shown (100× magnification). (G) BM cellularity was measured from more than eight different fields on days 10 and 21 using ImageJ software. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. and were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (n = 12, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). T-MSC CM, tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium; BM, bone marrow; BMT, bone marrow transplant; Bu–Cy, busulfan and cyclophosphamide; RBC, red blood cells; WBC, white blood cells.