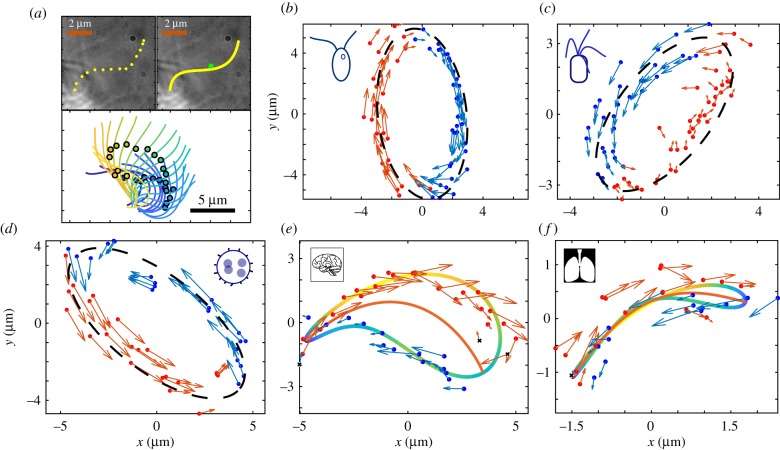
Figure 4.
Cilia in living organisms can be tracked, and from this a rower driving potential calculated to approximate their motion. (a) The flagella are tracked by interpolating between manually selected points along their length. A given flagellum is then approximated by its centre of drag following the steps laid out in [17]. (b) A tracked trajectory for a Chlamydomonas cell. The video of the Chlamydomonas is available from [4]. The colour indicates if the force at that point is considered positive or negative for the rower potential. The points are grouped by fitting an ellipse and then considering the major axis; points to the right are blue, and those left are red. The fitted ellipse is indicated by the black dashed line. (c) A similar trajectory for a quadri-flagellated alga; from [19]. (d) The centre of drag trajectory for a Volvox cell. One flagellum has been snipped, and the remaining flagellum is tracked. The Volvox videos are available from [17]. (e) A trajectory from a mouse brain epithelial cilium. This particular cilium is available from [38], but one other was sourced from [42]. The shape of the trajectory is no longer elliptical, but has a crescent shape. To group the forces as positive or negative a second-order Fourier series is fitted to the x and y points. This orbit is shown by the blue–green–yellow orbit, where the colour indicates the local speed along the trajectory. The central line within the fitted trajectory is then used to group the tracked points, where the endpoints are determined using the local speed. (f) The same process is applied to cilia from human airways. Videos of the airway cilia are from [39]. Some points were excluded when fitting driving potentials to the crescent trajectories, because the change in centre of drag was counter to the average force; these points are marked by black crosses. They result from variance in the trajectory size when tracking multiple cycles. A similar effect was seen in the Volvox cells, but it was consistent across multiple cycles and relates to conformation changes in the cilium. Consequently, the points were still included in the Volvox case.