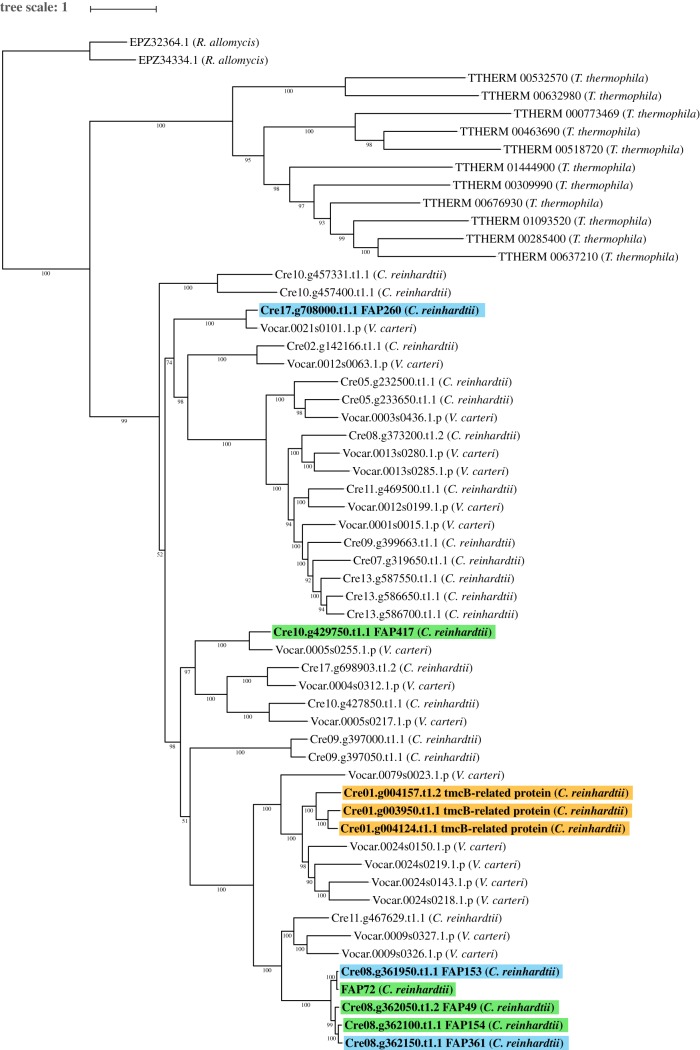
Figure 5.
Maximum-likelihood tree of C. reinhardtii PAS proteins and orthologues. Maximum-likelihood tree of C. reinhardtii flagellar-associated PAS proteins with high-confidence orthologues, rooted with R. allomycis as the outgroup. Green highlighting indicates C. reinhardtii PAS proteins predicted to be associated with the CA; orange highlighting indicates C. reinhardtii flagellar PAS proteins encoded on Chromosome 1; blue highlighting indicates other C. reinhardtii flagellar PAS proteins. For the tree construction only, a model for FAP72 was used that included the N-terminus of NCBI FAP72 (aa 1–471) joined to the N-terminus of Phytozome FAP72 (see Methods). The conjoined model lacks only 15 unmatched amino acids from the C-terminus of Phytozome FAP408. Phytozyme lists two transcripts for the Cre01.g004124 gene: Cre01.g004124.t1.1 (primary) and Cre01.g004124.t2.1; the former includes two amino acids not present in the latter and was used to construct this tree, whereas the latter is the one associated with this gene in the Chlamydomonas Flagellar Proteome Project (http://chlamyfp.org/index.php) and so is referred to in the main text. The tree was constructed with IQ-TREE [31] and was visualized using iTOL [34]. Support values show ultrafast bootstrap data with 1000 iterations [33]. Scale represents average number of substitutions per residue. (Online version in colour.)