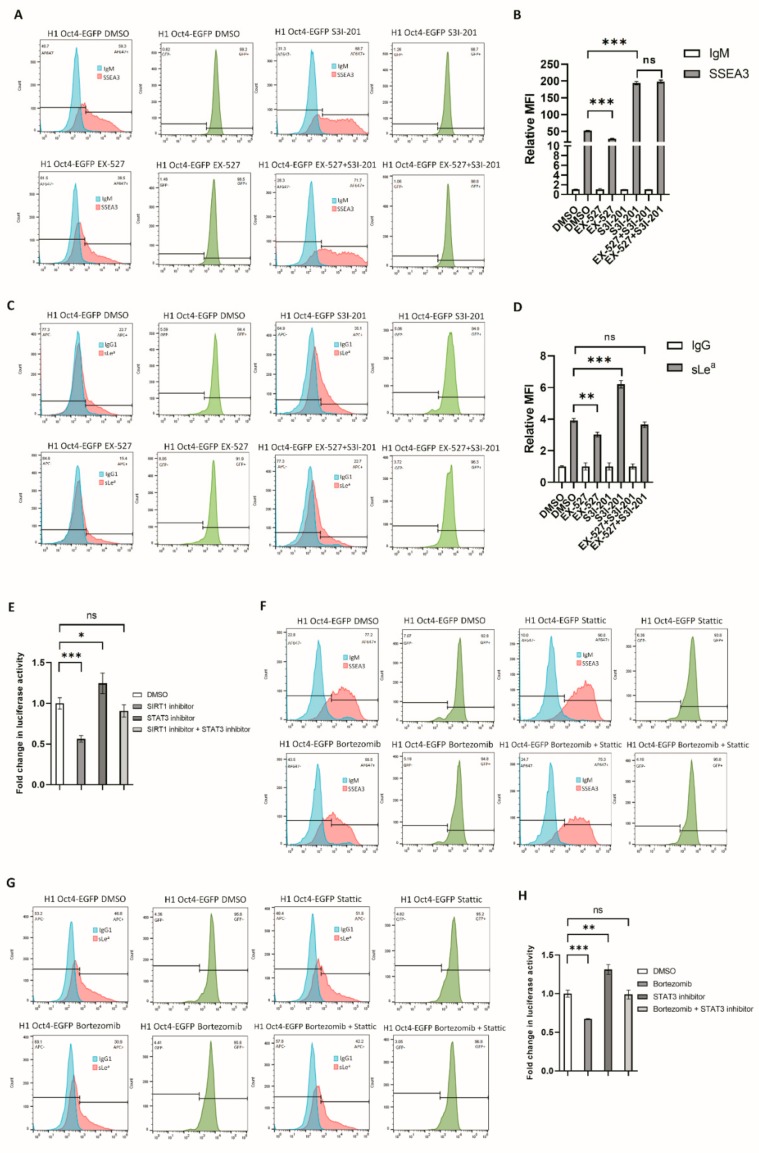
Figure 6.
SSEA3 and sialyl Lewis a synthesis is altered by SIRT1 or STAT3 inhibitors. (A) Flow cytometry showing the levels of SSEA3 on H1 Oct4-EGFP cells after treatment with a SIRT1 or STAT3 inhibitor. All treated cells had similar GFP signal intensities under G418 selection. (B) The MFI of stained SSEA3 compared with the control. EX-527, a SIRT1 inhibitor, repressed SSEA3 synthesis in H1 Oct4-EGFP cells, and S3I-201, a STAT3 inhibitor, activated SSEA3 expression. EX-527-mediated repression of SSEA3 synthesis was reversed by S3I-201 (***, p < 0.001 and ns: not statistically significant). (C) Flow cytometry showing the levels of sialyl Lewis a on H1 Oct4-EGFP cells after treatment with a SIRT1 or STAT3 inhibitor. All treated cells had similar GFP signal intensities under G418 selection. (D) The MFI of stained sialyl Lewis a compared with the control. EX-527-mediated repression of sialyl Lewis a synthesis was reversed by S3I-201 (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; and ns: not statistically significant). (E) EX-527 represses B3GALT5-LTR promoter activity in 2102Ep cells, and the EX-527-mediated repression of the B3GALT5-LTR promoter activity is reversed by S3I-201 (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; and ns: not statistically significant). (F) Bortezomib represses SSEA3 synthesis in H1 Oct4-EGFP cells, and this repression is reversed by Stattic. (G) Bortezomib represses sialyl Lewis a synthesis in H1 Oct4-EGFP cells, and this repression is reversed by Stattic. (H) Bortezomib represses B3GALT5-LTR promoter activity in 2102Ep cells, and the Bortezomib-mediated repression of the B3GALT5-LTR promoter activity is reversed by Stattic (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; and ns: not statistically significant).