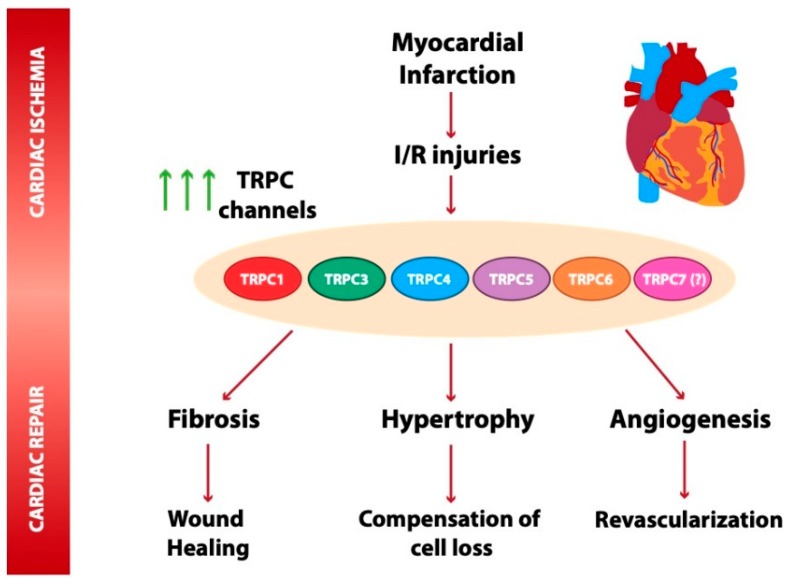
Figure 1.
Scheme summarizing transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channel isoforms dysregulated under myocardial infarction (MI) and ischemia and reperfusion. TRPC1, 3, 4, 5, and 6 are upregulated in mouse and rat animal models of MI [5,13,71]. Compelling evidence indicates that TRPC channel overexpression contributes to Ca2+ entry, mediating the activation of Ca2+-sensitive signaling pathways, such as calcineurin–NFAT, a critical pathway involved in apoptosis, cardiac hypertrophy, and fibrosis [13,28,55,66,67]. TRPC proteins are likely also involved in cardiac repair-related processes. The protective role played by TRPC6 in wound healing is of note [37]. Other studies suggested a role of TRPC channels, such as TRPC5, in angiogenesis and revascularization triggered post ischemia [104].