Figure 4.
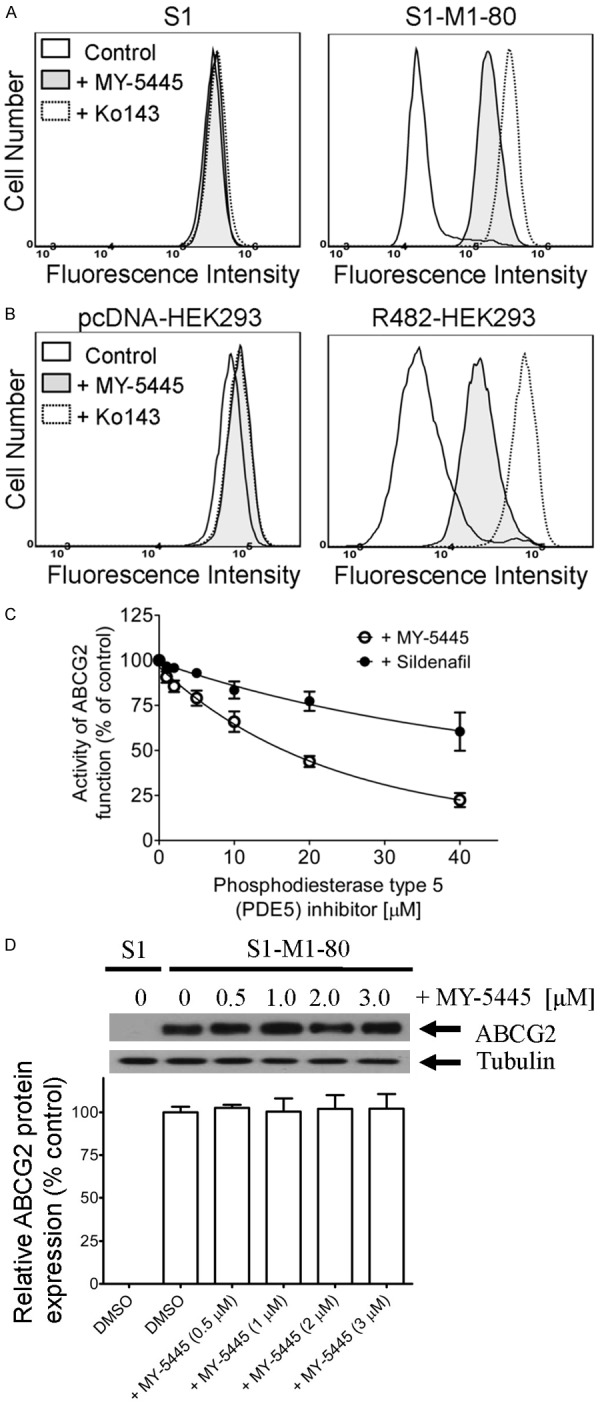
MY-5445 inhibits the drug transport function, but not the protein expression of ABCG2. The accumulation of fluorescent pheophorbide A (PhA) in human S1 colon cancer cells (A, left panel) and ABCG2-overexpressing variant S1-M1-80 cancer cells (A, right panel), as well as in HEK293 cells (B, left panel) and HEK293 cells transfected with human ABCG2, R482-HEK293 (B, right panel), was measured in the presence of DMSO (solid lines) or 10 μM of MY-5445 (solid lines, filled) or 1 μM of ABCG2 reference inhibitor Ko143 (dotted lines), and analyzed immediately by flow cytometry as described previously [71]. Representative histograms of three independent experiments are shown. (C) The concentration-dependent inhibition of ABCG2-mediated efflux of PhA by phosphodiesterase inhibitors MY-5445 (open circles) and sildenafil (filled circles) in R482-HEK293 cells. Values are presented as mean ± SEM calculated from at least three independent experiments. (D) Human S1-M1-80 colon cancer cells were treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or increasing concentrations (0.5-3.0 μM) of MY-5445 for 72 h, and the protein expression of human ABCG2 was analyzed by western blotting according to the method described previously [70]. α-Tubulin was used as an internal loading control. Values are presented as mean ± SEM calculated from three independent experiments.
