Figure 7.
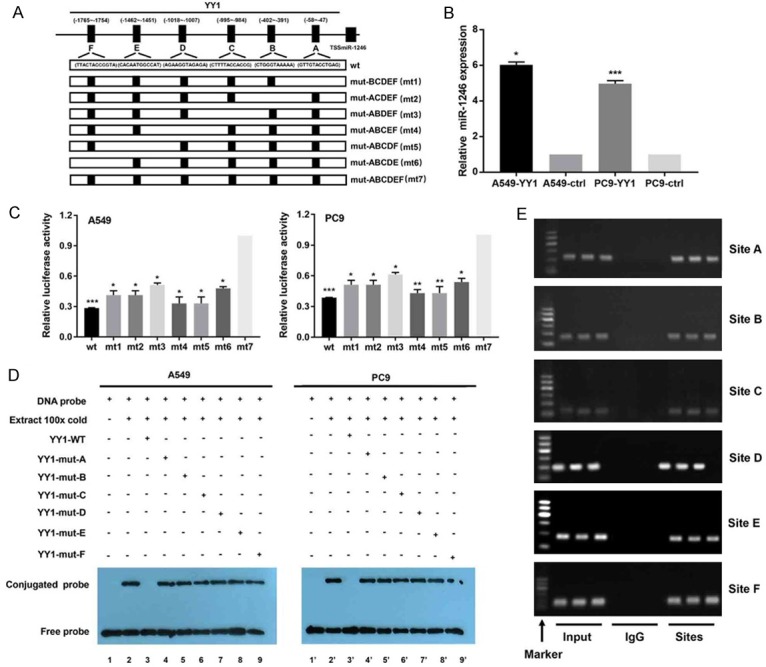
YY1 increases miR-1246 expression by binding to its promoter region. A. The informal structure of the miR-1246 promoter regions sites binding with the YY1. The wild-type (wt) showing the joint sequences and the mutant (mt) ones were introduced to luciferase reporters driven by the promoter. B. The relative miR-1246 expression (n=3) after YY1 overexpression or not was detected by qRT-PCR in NSCLC cells. ctrl: control. C. The dual-luciferase plasmids containing the indicated wt and mts sequences reports were transfected into A549 and PC9 for luciferase activity assays (n=3). Data were presented as the mean ± SD. D. EMSA results for the verification of YY1 binding sites (n=3). Nuclear proteins were extracted from A549 and PC9 cells. Cell lines 1 and 1’ were assessed by the labelled free probe as a control. Cell lines 3 and 3’ were tested with a 100-fold excess of unlabeled wt probe, while cell lines 2 and 2’ were tested without any unlabelled competition. Cell lines 4~9 and 4’~9’ were tested with unlabelled mutants that competed with their respective labelled probes. E. Results from ChIP assays (n=3) using an antibody against YY1; the binding sites were identifed by PCR gel. The input was the positive control, and IgG was used as the negative control. The locations were determined by molecular weight as marker shown. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, ***, P<0.001. Data are presented as the mean ± SD.
