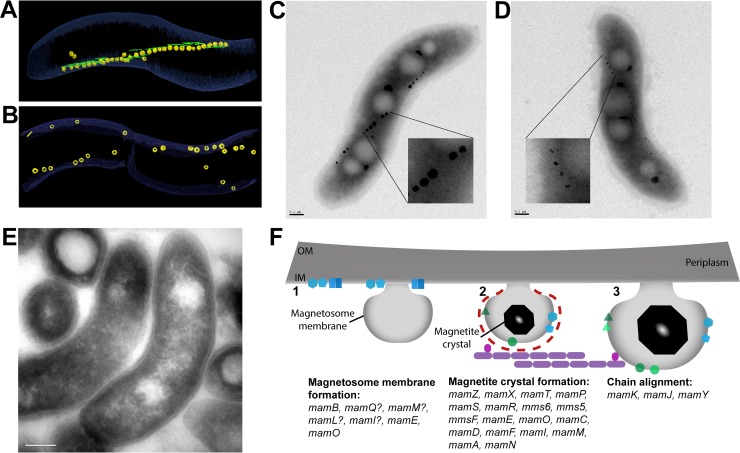
Fig 3. AMB-1 and MSR-1 strains with defects in magnetosome formation.
(A) Wild-type, AMB-1–cell image taken from segmentation of an electron cryotomogram. MamK filaments (green) run parallel to magnetosomes (yellow). (B) Electron cryotomogram image of a ΔmamK AMB-1 cell that shows disorganized magnetosomes. Images provided by Komeili. (C) TEM image of a wild-type, AMB-1 cell. Scale bar is 0.2 μm. Close-up of magnetosomes is magnified 6×. (D) TEM image of a ΔmamT AMB-1 cell showing small, misshapen magnetosomes. Scale bar is 0.2 μm. Close-up of magnetosomes is magnified 6×. Image provided by McCausland and colleagues. (E) TEM image of a cryosection of ΔmamL AMB-1 cells showing that magnetosome membranes are absent. Scale bar is 0.2 μm. Image provided by Komeili. (F) Diagram of the stepwise process of magnetosome formation and the proteins involved from membrane invagination (1), to crystal nucleation (2), and to membrane growth and formation of a mature magnetic crystal (3). Genes that have been found to be involved at each step are listed. AMB-1, Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1; IM, inner membrane; OM, outermembrane; MSR-1, Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1; TEM, transmission electron microscopy.