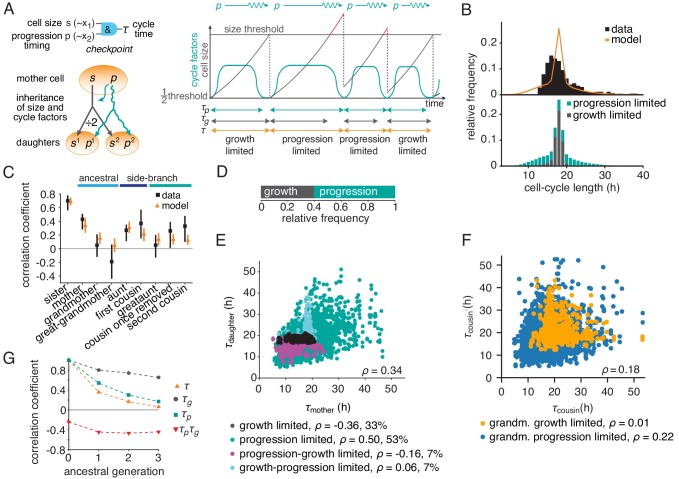
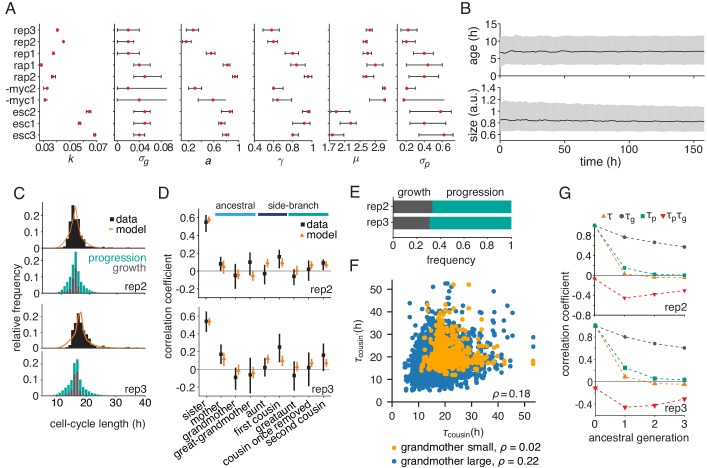
Figure 3. The growth-progression model.
(A) Scheme of the growth-progression model with heritable variables relating to cell size and cycle progression timing . (B) Measured and simulated cell-cycle length distributions (upper). Model distribution resolved by the division-limiting process (lower). (C) Measured and modeled correlation pattern with Spearman rank correlation coefficient and bootstrap 95%-confidence bounds. (D) Proportion of simulated cells limited by growth or progression. (E) Correlation of simulated mother-daughter cycle lengths colored by their division limitation: both by (black), both by (green), mother – daughter (magenta), mother – daughter (cyan). Percentage of cells in each subgroup and their correlation coefficients are shown. (F) Correlation of simulated cousin-cousin cycle length colored by the limitation of the common grandmother: by (orange) or (blue). (G) Autocorrelations along ancestral line of cycle length , growth time and the progression time , and the cross-correlation .