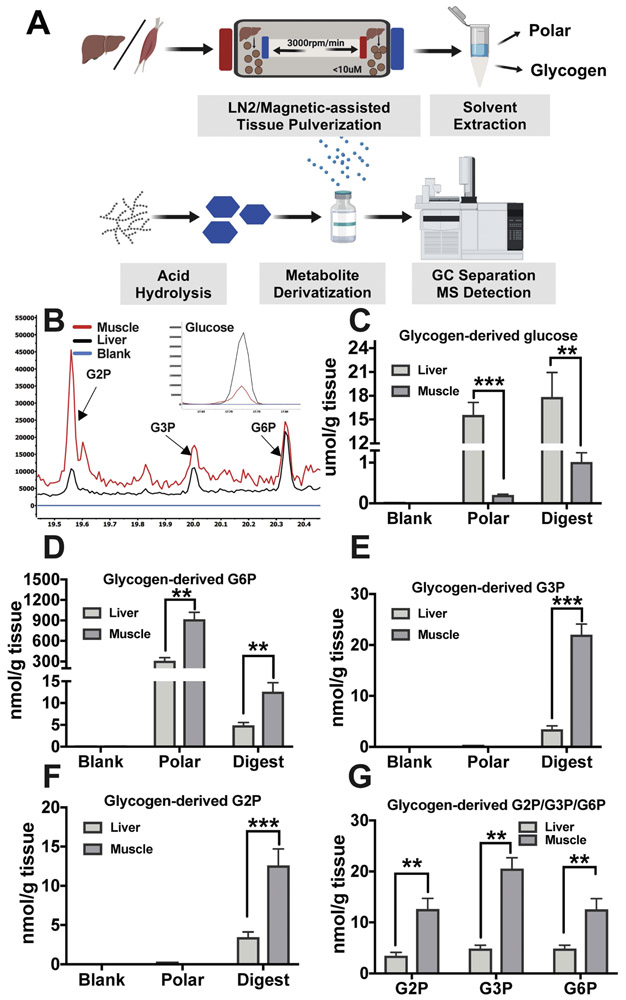
Figure 4: Extraction and GCMS analysis of liver and muscle glycogen.
(A) Schematics of glycogen extraction: mouse liver or skeletal muscle were milled to 10μm particles by liquid N2 Freezer/Mill Cryogenics Grinder magnetic assisted tissue-grinding mill, followed by polar and organic solvent removal of free polar metabolites and lipids. Glycogen was then extracted by 10% TCA. Isolated glycogen was hydrolyzed to monomers by mild hydrolysis, derivatized by MEOX and MSTFA, and analyzed by GCMS (B).
Quantitation of liver or muscle derived glucose (C), G6P (D), G3P (E), G2P (F) the third wash of tissue pellet is served as blank, and free polar metabolite fraction serves as negative control for G3P and G2P and a positive control for G6P. (F) Muscle contains higher G2P, G3P and G6P than liver when standardized to tissue weight. Data shown in (C-G) are from three experiments and are shown as mean ±SEM.
* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001; two-tailed t-test.