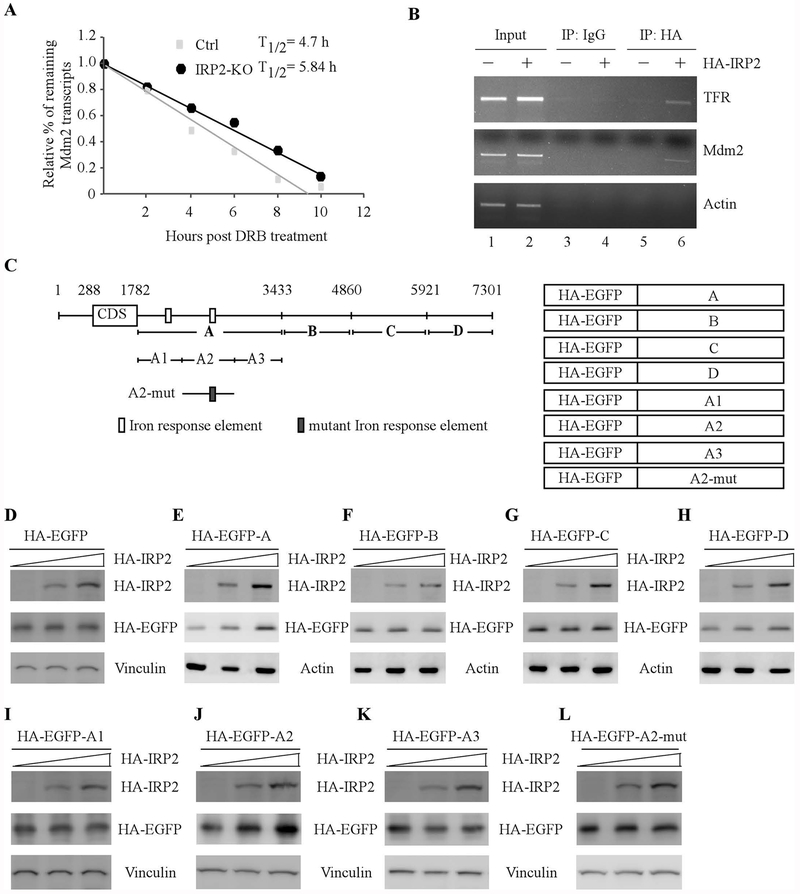
Figure 5.
IRP2 is required for Mdm2 mRNA stability via binding to the IRE in its 3’UTR. (A) The half-life of Mdm2 transcripts was measured in isogenic control and IRP2-KO p53−/−HCT116 cells treated with DRB for various times. The level of MDM2 transcript was normalized to that of GAPDH control and the relative half-life of MDM2 was calculated. (B) IRP2 associates with MDM2 transcript in vivo. H1299 cells were uninduced or induced to express HA-tagged IRP2, followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-HA or an isotype control IgG. RT-PCR analysis was performed to measure the level of TFR, MDM2 and GAPDH transcripts in the control and IRP2-RNA immunocomplexes. (C) Schematic representation of the Mdm2 transcript, the locations of IREs as well as the reporters containing various lengths of Mdm2 3’UTRs. (D-H) p53−/− HCT116 cells were transiently transfected with various amounts of IRP2 expression vector and a fixed amount of EGFP expression vector alone (D) or a EGFP vector fused with Mdm2-3’UTR-A (E), Mdm2-3’UTR-B (F), Mdm2-3’UTR-C (G), or Mdm2-3’UTR-D (H). Twenty-four hours posttransfection, the levels of IRP2 (D-H), EGFP (D-H), vinculin (D), and actin (E-H) proteins were examined by western blot analysis. (I-L) The experiments were performed as in (D-H) except that an EGFP vector fused with Mdm2-3’UTR-A1 (I), Mdm2-3’UTR-A2 (J), Mdm2-3’UTR-A3 (K), or Mdm2-3’UTR-A2-M (L) were used.