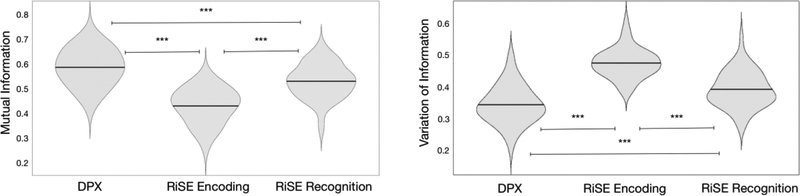
Figure 4:
Mutual information (left) and Variation of Information (right) scores quantifying the similarity of module partitions between high and low cognitive control conditions in the DPX, RiSE encoding, and RiSE recognition tasks. The horizontal line inside each violin indicates the mean. *** indicates p < 0.001. Subsequent examination of network specific Variation of Information scores of cognitive systems exhibiting within network control effects (FPN, Vat, Visual Networks) was performed. A repeated measures ANOVA identified a main effect of task (F(2,102) = 49.537, p <0.001) and main effect of network (F(2,102) = 19.965, p <0.001) indicating that the extent of network reorganization differed across tasks and networks. Post-hoc t-tests revealed that Variation of Information was greater in the FPN and VAt compared to the Visual Network (t = 5.897, p <0.001 and t = 5.254, p <0.001 respectively), but there was no difference between the FPN and VAt.