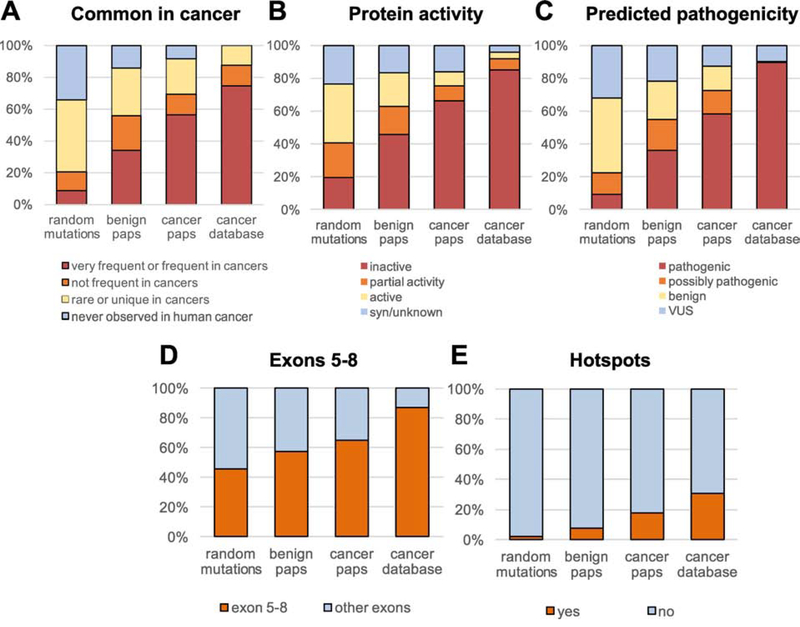
Figure 4. Comparison of TP53 mutations identified in Pap tests from women with and without HGSC vs. random TP53 mutations and TP53 mutations in the cancer database.
Mutations were compared based on (A) common appearance in cancers, (B) inactivation of protein activity, (C) predicted pathogenicity, (D) location in exons 5–8, and (E) location in hotspot codons. ‘Random mutations’ includes all possible mutations in the TP53 coding region (n=3,546), benign Paps include 127 mutations, cancer Paps include 94 mutations, and cancer database includes all TP53 mutations identified in human cancers in the April 2017 version of the UMD cancer database (n=71,051).