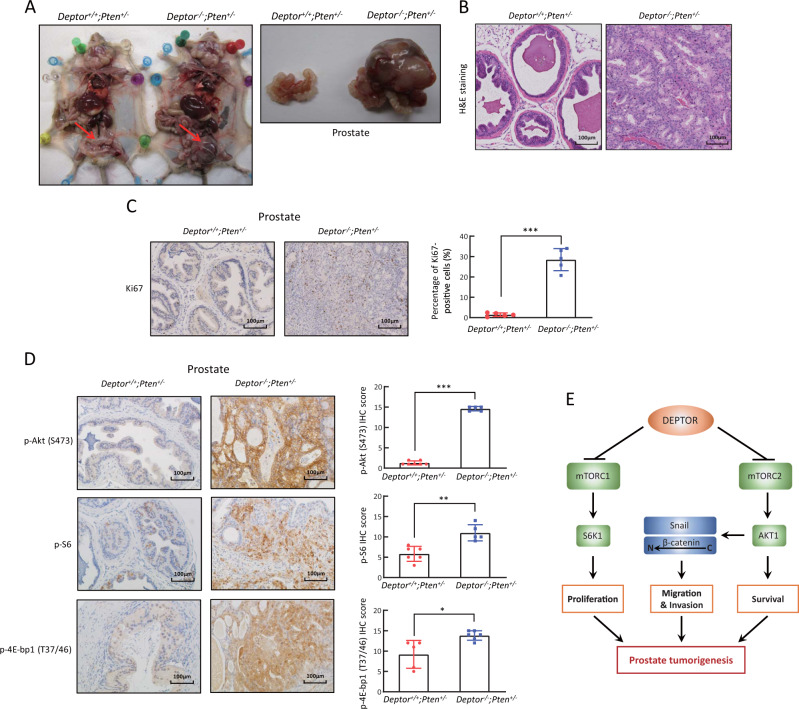
Fig. 6.
Deptor knockout induces prostate tumorigenesis triggered by Pten heterozygous loss via the activation of mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling in mice. a Deptor knockout causes prostate tumorigenesis triggered by Pten heterozygous loss. Representative images of the mice and prostate glands from three pairs of Deptor+/+;Pten+/− and Deptor−/−;Pten+/− littermate mice. b, c Excessive proliferation of epithelial cells in prostate cancer tissues from Deptor−/−;Pten+/− mice. The prostate tissues from Deptor+/+;Pten+/− and Deptor−/−;Pten+/− mice were sectioned and subjected to H&E staining (b) and Ki67 staining (c). d Deptor deletion activates mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling during prostate tumorigenesis. The prostate tissues from Deptor+/+;Pten+/− and Deptor−/−;Pten+/− mice were sectioned and subjected to immunohistochemical staining with the indicated antibodies. The staining quantification was determined by IHC scoring using an IRS system from at least five random fields of prostate tissue sections. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. e A model for DEPTOR suppression of prostate tumorigenesis