FIGURE 3.
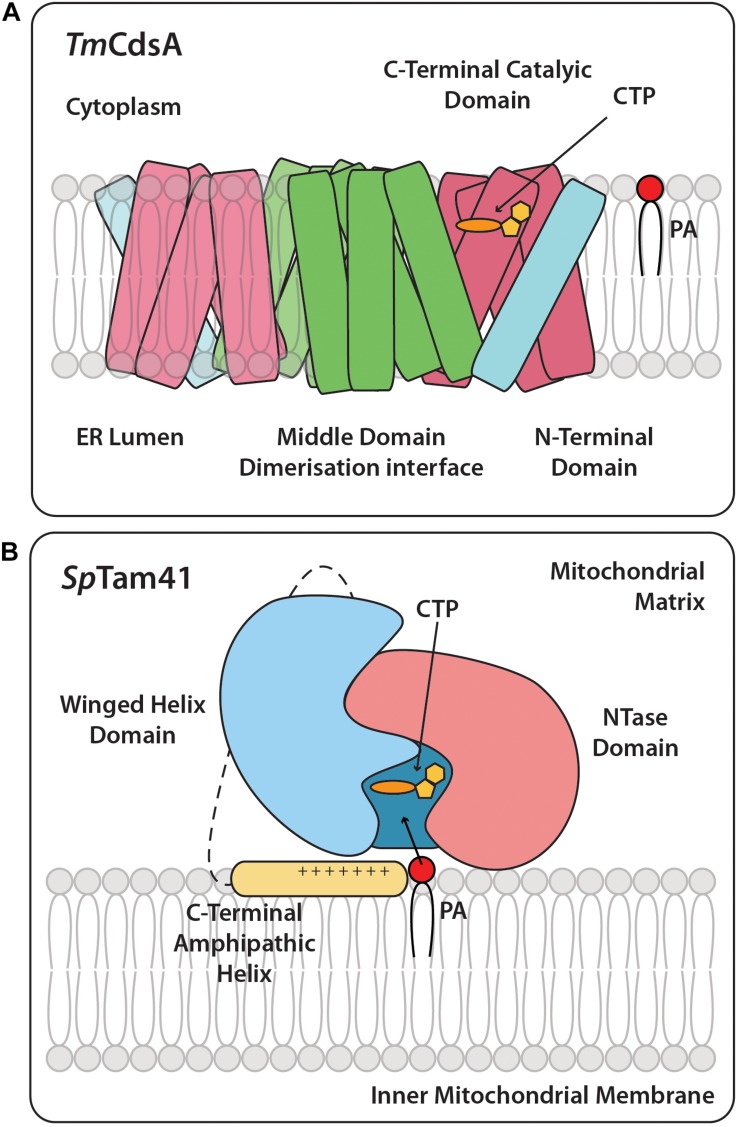
Cartoon structures of TmCdsA and SpTam41. (A) CDS is an integral membrane protein and is present as a dimer and accepts the two substrates, CTP, and PA. On the cytoplasmic side of each TmCdsA monomer, a funnel-shaped cavity indents half way into the membrane region. The cavity has two wide openings, which enable it to receive dual substrates, CTP from the cytoplasm and PA from the lipid bilayer at the same time. The conversion of CTP and PA into CDP-DAG and pyrophosphate occurs through a process involving the transfer of CMP group from CTP onto the phosphate group of PA. Adapted from Liu X. et al. (2014). Color coding is the same as TmCdsA in Figure 2. (B) The full length SpTam41 exists as a monomer and is associated to the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane by the membrane binding domain at the C-terminal region (colored yellow). CTP and PA sequentially bind to the active site of Tam41. The enzymatic conversion of CTP and PA into CDP-DAG and pyrophosphate occurs through a process involving the transfer of CMP group from CTP onto the phosphate group of PA. Adapted from Jiao et al. (2019). Color coding is the same as SpTam41 in Figure 2.