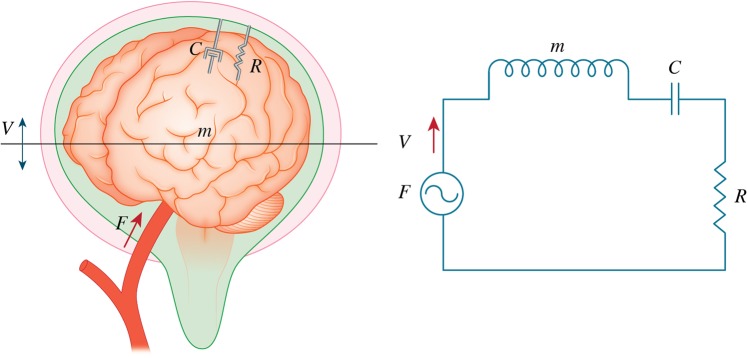
Figure 5.
Theoretical analysis of the resonance phenomenon in the skull. Left: the schema of the simple brain acoustic dynamics model. The brain (weight: m kg) is located in the closed space. The CSF interferes with the movement of the brain by the effect of a shock absorber (cerebrospinal volumetric compliance: C F) and viscosity (resistance: R Ω). The arterial pulse (force: f N) moves the brain. The moving speed of the brain is velocity: v m/s. Right: mechanodynamically electrically equivalent circuit (weight: m kg) (condenser: C F) (resistance: R Ω) (force: f N).