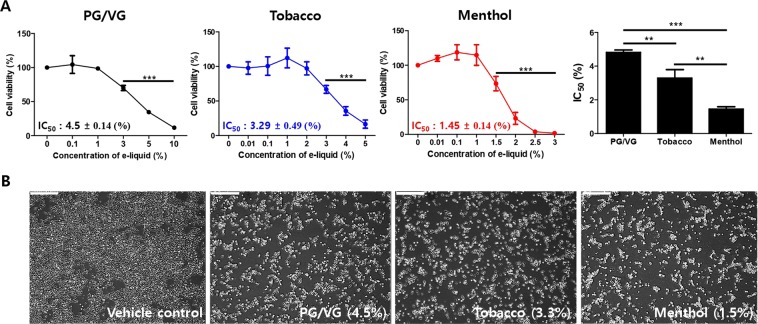
Figure 1.
E-liquid reduced cell viability of HMEECs in a dose-dependent manner. (A) HMEECs were treated with PG/VG, tobacco- and menthol-flavored e-liquids for 24 h in a various concentration of e-liquid (0.01 to 10%). The control group was not exposed to e-liquids. The cellular cytotoxicity was determined by cell counting assay in HMEECs. Cell viability was reduced by exposure to e-liquids in a dose-dependent manner. The multiple independent experiments were performed (n = 6) and the average IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) values were calculated using the ED50 plus v 1.0 software and showed as mean ± SD (PG/VG: 4.5 ± 0.14, tobacco-flavored: 3.29 ± 0.49, and menthol-flavored: 1.45 ± 0.14). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared to the corresponding control. (B) HMEEC morphology after exposure to the average IC50 values of each e-liquid for 24 h (PG/VG: 4.5%, Tobacco: 3.3%, and Menthol: 1.5%). Vehicle control is untreated HMEECs. E-liquids-treated groups showed 50% cell death compared to the control group.