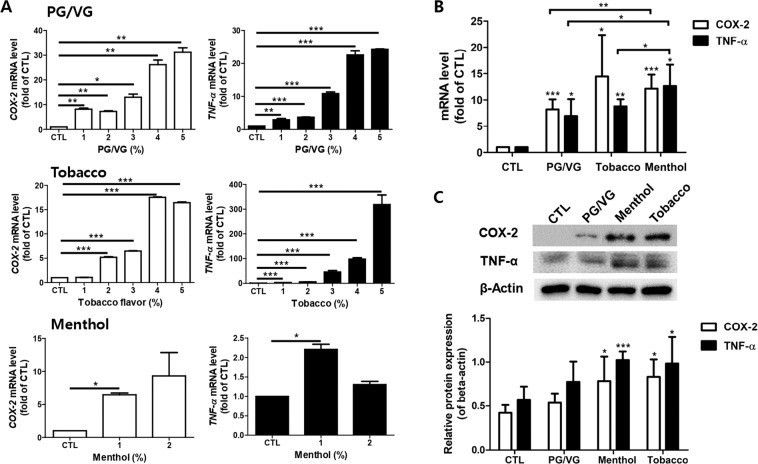
Figure 2.
E-liquids stimulated the expression of inflammatory cytokines in HMEECs. (A) HMEECs were treated with PG/VG (1 to 5%), tobacco-flavored e-liquid (1 to 5%), and menthol-flavored e-liquid (1 and 2%) for 24 h. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to evaluate inflammatory cytokine gene such as COX-2 and TNF-α expression levels. The expression levels of COX-2 and TNF-α significantly increased in e-liquid-concentration-dependent manner. (B) Cells were exposed to the average IC50 values of each e-liquid for 24 h (PG/VG: 4.5%, Tobacco: 3.3%, and Menthol: 1.5%). Both flavored e-liquids significantly increased the mRNA levels of COX-2 and TNF-α on HMEECs. mRNA expression of COX-2 and TNF-α was significantly increased in menthol-flavored e-liquid-treated group compared to in PG/VG group. (C) Cells were treated with PG/VG (4.5%), tobacco-flavored e-liquid (3.3%), and menthol-flavored e-liquid (1.5%) for 24 h. The results showed that the levels of COX-2 and TNF-α protein levels were increased by treatment with e-liquids. Densitometric analysis of western blot is shown as a graph. Similar to their mRNA profiles, COX-2 and TNF- α protein expression was significantly higher following tobacco- and menthol-flavored e-liquid exposure compared to the control group. Western blot data were quantified and normalized to β-actin levels. All data were obtained from three independent experiments and the error bars indicate the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared to the corresponding control.