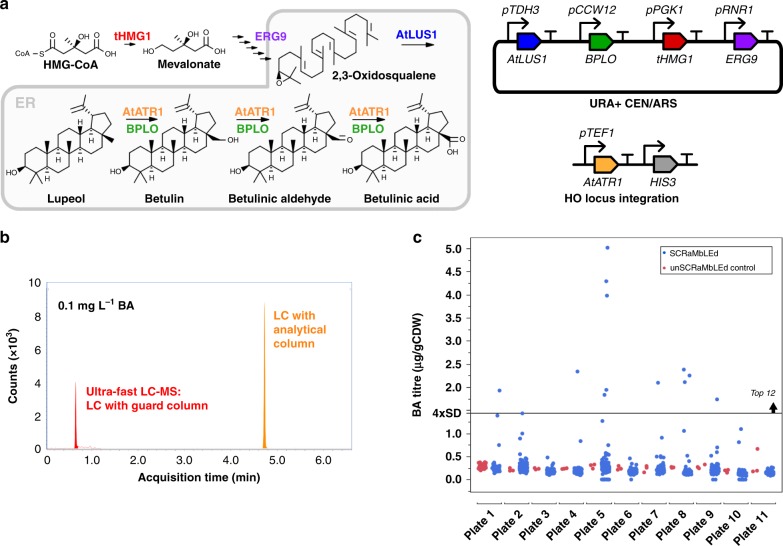
Fig. 1. SCRaMbLE of a betulinic acid-producing strain followed by rapid screening yields a diverse library.
a BA is synthesised by redirecting flux from the endogenous mevalonate pathway (left, top row) using three heterologous enzymes (AtLUS1, a lupeol synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana; BPLO, a cytochrome P450 from Betula platyphylla; and AtATR1, a P450 reductase from Arabidopsis thaliana). tHMG1 and ERG9 were additionally introduced to increase flux down the mevalonate pathway. Four genes (AtLUS1, BPLO, tHMG1, and ERG9) were expressed from a URA+ CEN/ARS plasmid while AtATR1 was integrated into the genome at the HO locus on chromosome IV (right). b Ultra-fast LC-MS utilises only a guard column for separation (red) which analyses each sample with a retention time of 40 s compared to ~4.8 min for conventional LC-MS (orange). c Eleven plates were run with ultra-fast LC-MS over 26 cumulative hours split across 2.5 days. Forty pre-SCRaMbLE control samples (red) were present in the first plate and three in every subsequent plate. Standard curves were run at the start and the end of the screen. After screening 964 SCRaMbLE colonies a minimum OD600 cut off of 0.1 was applied. 914 SCRaMbLE strains exceeded this threshold and were plotted (blue). A threshold of above ×4 control standard deviations was set to identify significantly improved strains. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.