Figure 2.
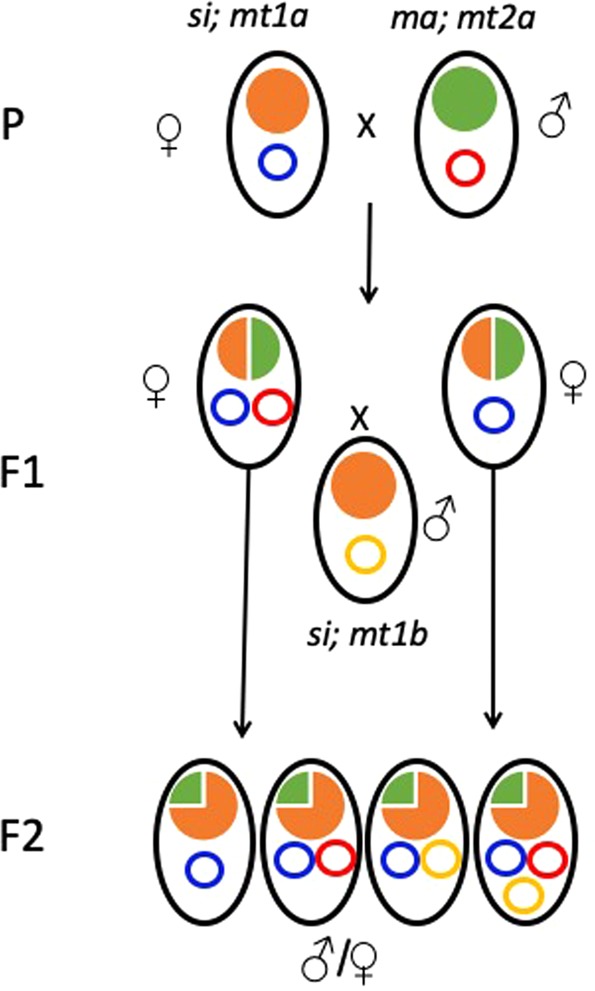
The experimental outline of the crosses of this study. Ellipses with black outline represent individuals. Within these ellipses are drawn the nuclear DNA (solid circles) and mtDNA (open circles). The color of the circles indicate the percentage of the nuclear genome that belong to D. simulans (orange) or to D. mauritiana (green). The color of the smaller circles indicate the origin of the mtDNA; blue and yellow are the different mitotypes of D. simulans, and red is the mtDNA for D. mauritiana. In the paternal generation (P) pure species are crossed. All hybrids in F1 generation have 50% of the nuclear DNA from the maternal and 50% of the paternal species. Mitochondrially there can be two types of individuals (female only are shown); either heteroplasmic (right ellipsis) or homoplasmic (left ellipsis). F1 female hybrids were crossed one-by-one with D. simulans males. After crossing the F1 females were stored in ethanol. F1 males were also stored in ethanol. Τhe F2 individuals have been produced by the backcross of F1 female with the paternal species (D. simulans) containing a different mitotype (yellow circle) from the female in P generation. Their nuclear DNA is consisted by 25% of D. mauritiana and 75% of D. simulans. Mitochondrially, there are four possible situations (ellipses in F2 generation from left to right); homoplasmic for the common maternal mtDNA (blue), heteroplasmic that have inherited their heteroplasmy from their mother (blue and red), heteroplasmic with the common maternal (blue) and the paternal (yellow) mtDNA and heteroplasmic containing both the common (blue) and the rare (red) maternal haplotypes and the paternal haplotype (yellow). F2 males and females were stored in ethanol.
