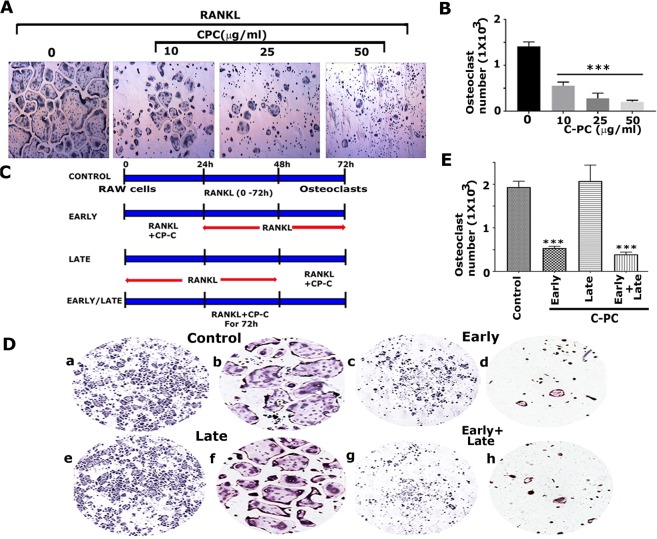
Figure 1.
Analysis of the effect of C-PC on RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. (A) Effect of different doses of C-PC (10, 25, and 50 µg) on osteoclast differentiation. Phase-contrast microscopy images of TRAP stained osteoclasts are shown at indicated doses. Magnification is 4X. (B) The number of TRAP +ve multinucleated osteoclasts were counted in osteoclasts untreated (0) or treated with 10, 25, and 50µg C-PC for 72 h. Statistical analysis was performed to determine the dose-dependent inhibitory effect of C-PC on osteoclasts differentiation as compared with control untreated (0) cells. (C) Identification of the time-dependent effect of RANKL and C-PC on the osteoclast differentiation. The diagrammatic sketch demonstrates the treatment strategy of RAW cells with RANKL and C-PC (25 µg/ml). (D) Representative images of TRAP stained osteoclasts in response to the treatment strategy shown in panel C.TRAP stained osteoclasts in panels a,c,e, and g were taken with 4X objective (magnification: X40), while panels in b,d,f, and h were taken with 10X objective (magnification: X100). (E) The number of TRAP +ve multinucleated osteoclasts were counted in all treatment groups. Statistical analysis was performed to compare the number in the treatment groups to the control group. One-way ANOVA was applied, and values were expressed as mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001.